JUMP TO TOPIC
 In defining what is y intercept, we need to take note of the graph of a function. The y-intercept of any given function is the point where the graph touches the y-axis. Thus, the y-intercept of a graph is the point $(0,b)$ where $b$ is the value in the y-axis where the graph crosses.
In defining what is y intercept, we need to take note of the graph of a function. The y-intercept of any given function is the point where the graph touches the y-axis. Thus, the y-intercept of a graph is the point $(0,b)$ where $b$ is the value in the y-axis where the graph crosses.
It is important to solve for the y-intercept of a function because it helps in graphing lines since we already know at what point will the graph cut the y-axis. Moreover, y-intercepts are helpful in other applications of problems involving linear equations.
There are two types of intercepts in a function — we have the x-intercept and y-intercept. Intercepts, in general, are the points where the graph of the function crosses the x-axis or the y-axis. But in this article, we will focus on solving for the y-intercept of a given graph, a given equation, and given any two points in the graph.
How To Find Y-intercept on a Graph
Example 1
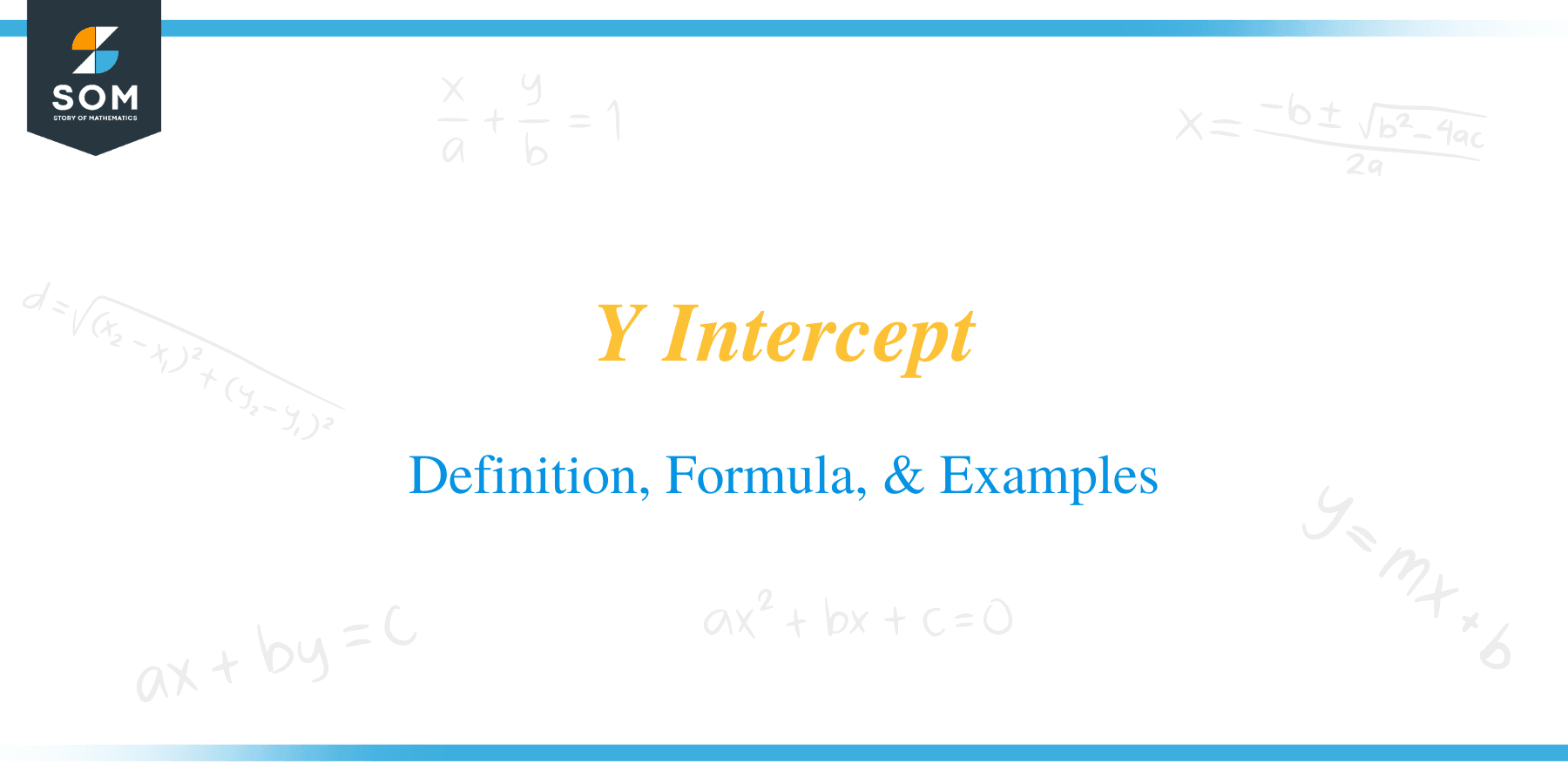
- Notice that the graph in Figure 1, the graph of $y=4x-6$, is a linear function that touches the y-axis at the point $(0,-6)$. Thus, the y-intercept of the linear graph $y=4x-6$ is located at the point $(0,-6)$.
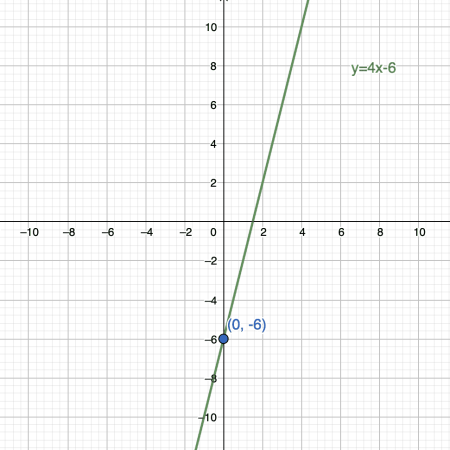
- The graph of the equation $y=8-x^2$ is a parabola. It intersects the y-axis exactly at the point $(0,8)$. Hence, the y-intercept of the parabola $y=8-x^2$ is at the point $(0,8)$.
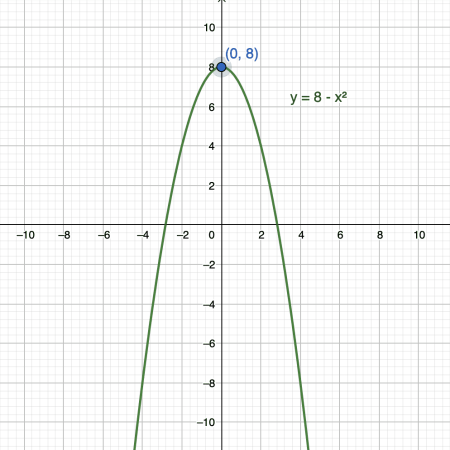
- The graph of exponential function $y=1-e^x$ in Figure 3 crosses the y-axis only at the origin and no other point. Therefore, the y-intercept of the given graph is at $(0,0)$.
Since we already know how to find y-intercept on a graph, the question now is, “Is it possible for a graph to have no y-intercept?”
Are There Graphs With No Y-intercept?
Yes, it is possible for a graph to have no y-intercept — this means that the graph does not touch the y-axis.
Note that a function satisfies a vertical line test. That is, if we are to draw infinite vertical lines in the graph, each line should touch the graph at most once. Since the y-axis is a vertical line, then the graph touches the y-axis either once or not at all. Moreover, we could note from this that it is not possible for a graph of a function to have more than one y-intercept.
Let’s look at the example of graphs that do not have y-intercepts below.
Example 2
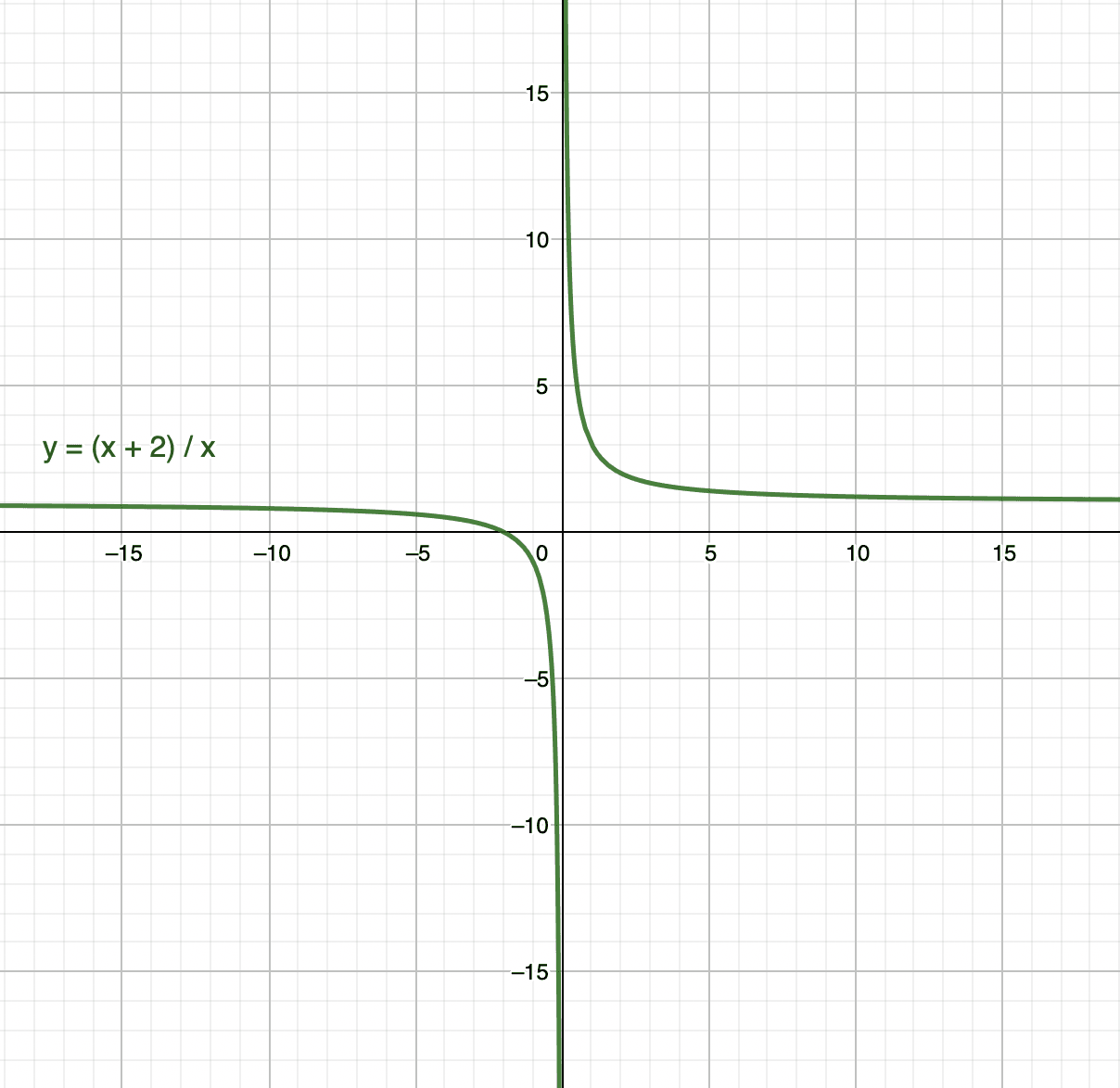
- In Figure 4, the behavior of the graph of $y=\dfrac{x+2}{x}$ grows closer and closer to the y-axis but never touches it. This is called an asymptote. It does look like it intersects or will intersect the y-axis after some point but if we look closely at the graph, we can see that it does not touch the y-axis no matter how close it will get.
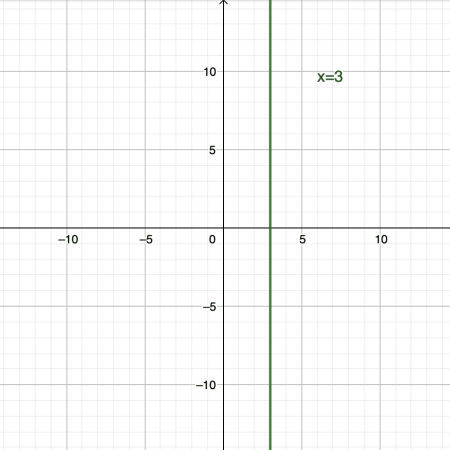
- The graph of $x=3$ is a vertical line that passes through the point $(3,0)$. The graph of $x=3$ is parallel to the y-axis, thus it is not possible for this graph to cross the y-axis at any point.
In conclusion, a graph does not always necessarily have a y-intercept. Graphs that are asymptotic to the y-axis and graphs that consist of a vertical line not passing through the origin do not have y-intercepts.
Now that we have geometrically identified a y-intercept in any given graph, let’s proceed to learning how to find them even when the graph is not plotted for us.
Solving for the Y-intercept of a Given Function
Even when we have no idea what the graph of a certain function looks like, we can still determine the y-intercept of that function. Remember that one of the roles of the y-intercept is that it helps describe the graph by determining at what point the graph will intersect the y-axis.
Observing the obtained y-intercept from previous examples, we get that the y-intercept of a function is the point with the form $(0,b)$. Thus, we can get the value of $b$ when we substitute $x$ for zero, then find the value of $y$. Note that the graph crosses the y-axis whenever $x=0$. Therefore, for any given function $y=f(x)$, the y-intercept of the function is at the point $(0,f(0))$.
However, in cases where the function is not defined at $x=0$, the function has no y-intercept.
Example 3
We verify the y-intercepts we get from the previous example.
- Let $y=4x-6$. When $x=0$, we have:
\begin{equation*}
y=4(0)-6=0-6=-6.
\end{equation*}
Thus, the y-intercept is the point $(0,-6)$.
- Consider the function $f(x)=8-x^2$. At $x=0$, the value of $f(0)$ is:
\begin{align*}
f(0)=8-0^2=8-0=8.
\end{align*}
This means that the function has y-intercept of $(0,8)$.
- The function $y=1-e^x$ has y-intercept at the origin, $(0,0)$, because when $x=0$, the value of the y-coordinate is:
\begin{align*}
y=1-e^0=1-1=0.
\end{align*}
Hence, even without the graph, we will still get the same y-intercept by substituting zero for the value of $x$.
Example 4
Example 5
Y-intercept of Polynomial Function
In general, if we have a polynomial function of some degree $n$,
$$f(x)=a_n x^n+a_(n-1) x^(n-1)+\cdots+a_2 x^2+a_1 x+a_0,$$
where $a_i$, for $i=0,1,2,\dots,n$ are real coefficients of the polynomial, then the y-intercept of the polynomial function $f$ is the point $(0,a_0)$.
Example 6
Given the function $f(x)=x^3-7x^2+9$. The function is a polynomial function, thus the y-intercept of the given polynomial function is $(0,9)$.
How To Find Y-intercept From Two Points
In finding the y-intercept of a graph given two points in the line, we have to solve for the equation of the line in the slope-intercept form.
Note that in a linear equation of the form:
$y=mx+b,$
the slope of the line is $m$ and the y-intercept is at $(0,b)$.
So, if we have two points $A(x_1,y_1)$ and $B(x_2,y_2)$, the slope of the line passing through these points is given by:
$m=(y_2-y_1)/(x_2-x_1 ).$
After solving for the slope $m$, we only have to find the value of $b$. So we take one of the points, say $A(x_1,y_1)$, and substitute it for the values of $x$ and $y$.
$y_1=mx_1+b$
Solving for $b$, we have:
$b=y_1-mx_1.$
Then, we have the y-intercept at the point $(0,b)$.
Example 7
Conclusion
The use of y-intercepts is deemed significant in the higher applications of linear equations and other linear models. Hence, it is important that we know how to determine the y-intercept of a function be it in a graph, in an equation format, or a linear function represented by just two points.
- The y-intercept of the graph is the point where the graph of the function and the y-axis meets, and a graph that is asymptotic or parallel to the y-axis does not have a y-intercept.
- The y-intercept of any given function $f(x)$ is the point $(0,f(0))$.
- The y-intercept of any polynomial function $f(x)=a_n x^n+\cdots+a_1 x+a_0$ is $(0,a_0)$.
- A function has no y-intercept if the function is undefined at $x=0$.
- Given two points passing through a line, the y-intercept of the line is the point $(0,b)$, where $b=y_1-mx_1$ and $m=\dfrac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}$ is the slope of the line.
In this guide, we discussed and solved for y-intercept in different mathematical scenarios, we also learned the importance of the y-intercept. Understanding how it works can help you use it better for your own benefit, such as plotting data and solving for other unknown variables; just remember that once you have the y-intercept, you can find your other variable by using a formula and plugging in what you know.
