Figure 1
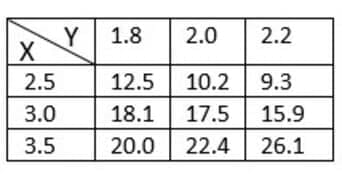
This problem aims to find the values of a function having alternate independent variables. A table is given to address the values of $x$ and $y$.
These formulas would be required to find the solution:
\[ f_x(x,y)=\lim_{h \to 0}\dfrac{f(x+h, y)-f(x,y)}{h}\]
\[ f_y(x,y)=\lim_{h\to 0}\dfrac{f(x, y+h)-f(x,y)}{h}\]
\[ f_{xy}=\dfrac{\partial}{\partial y}\left(\frac{\partial f}{\partial x} \right)=\dfrac{\partial}{\partial y}(f_x\]
Expert Answer:
Part a:
$f_x(3,2)$ $ f_x(x,y)=\lim_{h \to 0}\dfrac{f(x+h, y)-f(x,y)}{h} $ and considering $h=\pm 0.5$
\[ = \lim_{h \to 0}\dfrac{f(3 \pm 0.5, 2)-f(3,2)}{\pm 0.5}\]
Solving for $h=0.5$
\[ = \dfrac{f(3.5, 2)-f(3,2)}{0.5}\]
Using the table to plug in the functions values:
\[ = \dfrac{22.4-17.5}{0.5}\]
\[ = 9.8\]
Now solving for $h=-0.5$
\[ = \dfrac{f(2.5, 2)-f(3,2)}{-0.5}\]
Using the table to plug in the functions values:
\[ = \dfrac{10.2-17.5}{-0.5}\]
\[ = 14.6\]
Taking average of both $\pm 0.5$ answers for the final answer of $f_(3,2)$
\[ f_x(3,2)=\dfrac{9.8+14.6}{2}\]
\[ f_x(3,2)= 12.2\]
Part b:
$f_x(3,2.2)$
\[ f_x(3,2.2)=\lim_{h \to 0}\dfrac{f(3 \pm 0.5, 2.2)-f(3,2.2)}{\pm 0.5} \]
Solving for $h=0.5$
\[ = \dfrac{f(3.5, 2.2)-f(3,2.2)}{0.5}\]
Using the table to plug in the functions values:
\[ = \dfrac{26.1-15.9}{0.5}\]
\[ = 20.4\]
Now solving for $h=-0.5$
\[ = \dfrac{f(2.5, 2.2)-f(3,2.2)}{-0.5}\]
Using the table to plug in the functions values:
\[=\dfrac{9.3-15.9}{-0.5}\]
\[=13.2\]
Taking average of both $\pm 0.5$ answers for the final answer of $f_(3,2)$
\[f_x(3,2.2)=\dfrac{20.4+13.2}{2}\]
\[f_x(3,2.2) = 16.8\]
Part c:
$f_xy(3,2)$
\[f_{xy}(x,y)=\dfrac{\partial}{\partial y}\left( \frac{\partial f}{\partial x}\right)=\dfrac{\partial}{\partial y} (f_x)\]
\[=\lim_{h \to 0}\dfrac{f_x(x, y+h)-f_x(x,y)}{h}\]
\[f_{xy}(3,2)=\lim_{h \to 0}\dfrac{f_x(3, 2+h)-f_x(3,2)}{h}\]
Considering $h=\pm 0.2$
Solving for $h=0.2$
\[=\dfrac{f_x(3, 2.2)-f_x(3,2)}{0.2}\]
Plugging in the answers from part a and part b:
\[=\dfrac{16.8-12.2}{0.2}\]
\[=23\]
Now solving for $h=-0.2$
\[=\dfrac{f_x(3, 1.8)-f_x(3,2)}{-0.2}\]
Solving $f_x(3, 1.8)$ for $h=\pm 0.5$
Solving for $h=0.5$
\[f_x(3,1.8)=\lim_{h \to 0}\dfrac{f(3 \pm 0.5, 1.8)-f(3,1.8)}{\pm 0.5}\]
\[=\dfrac{f(3.5, 1.8)-f(3,1.8)}{0.5}\]
Using the table to plug in the functions values:
\[=\dfrac{20.0-18.1}{0.5}\]
\[= 3.8 \]
Now solving for $h=-0.5$
\[= \dfrac{f(2.5, 1.8)-f(3,1.8)}{-0.5} \]
Using the table to plug in the functions values:
\[= \dfrac{12.5-18.1}{-0.5} \]
\[= 11.2 \]
Taking average of $\pm 0.5$ answers for the final answer of $f_x(3,1.8)$
\[f_x(3,1.8) = \dfrac{3.8+11.2}{2}\]
\[f_x(3,1.8) = 7.5\]
Substituting $f_x(3,1.8)$ in the main equation above to find $f_{xy}(3,2)$
$f_{xy}(3,2)$ for $h = -2$ becomes:
\[= \dfrac{f_x(3, 1.8)-f_x(3,2)}{-0.2} \]
Plugging in the values:
\[= \dfrac{7.5-12.2}{-0.2} \]
\[= \dfrac{7.5-12.2}{-0.2} \]
\[= 23.5 \]
Taking Average of $ h=\pm 0.2$ answers to find the final answer:
\[f_{xy}(3,2) = \dfrac{23+23.5}{2}\]
\[f_{xy}(3,2) = 23.25\]
Numerical Results:
Part a: $f_x(3,2) = 12.2$
Part b: $f_x(3,2.2) = 16.8$
Part c: $f_{xy}(3,2) = 23.25$
Example
For the given table, find $f_y(2.5, 2)$.
\[ f_y(x,y) = \lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{f(x, y+h)-f(x,y)}{h} \]
Plugging the values in:
\[ f_y(2.5,2) = \lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{f(2.5, 2+h)-f(2.5,2)}{h} \]
Solving for $h = \pm 0.2$
For $h = 0.2$
\[ = \dfrac{f(2.5, 2.2)-f(2.5,2)}{0.2} \]
Using the table to plug in the function values:
\[= \dfrac{9.3 – 10.2}{0.2} \]
\[= -4.5 \]
Now solving for $h=-0.2$
\[= \dfrac{f(2.5, 1.8)-f(2.5,2)}{-0.2} \]
Using the table to plug in the functions values:
\[= \dfrac{12.5-10.2}{-0.2} \]
\[= – 11.5 \]
Taking average of $\pm 0.5$ answers for the final answer of $f_y(2.5,2)$:
\[f_y(2.5,2) = \dfrac{-4.5-11.5}{2}\]
\[f_y(2.5,2) = -8\]
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
