JUMP TO TOPIC
Square Root of 256 + Solution With Free Steps
The symbol for the square root of 256 is √256. √256 = 16 is another way to express the concept. Because square and square root are opposites of each other, 256 is the square of 16. 256 is a perfect square.
In this article, we will analyze and find the square root of 256 using various mathematical techniques, such as the approximation method and the long division method.
What Is the Square Root Of 256?
The square root of the number 256 is 16.
The square root can be defined as the quantity that can be doubled to produce the square of that similar quantity. In simple words, it can be explained as:
√256 = √(16x 16)
√256 = √(16)$^2$
√256 = ±16
The square can be canceled with the square root as it is equivalent to 1/2; therefore, obtaining 16. Hence 16 is 256’s square root. The square root generates both positive and negative integers.
How To Calculate the Square Root of 256?
You can calculate the square root of 256 using any of two vastly used techniques in mathematics; one is the Approximation technique, and the other is the Long Division method.
The symbol √ is interpreted as 256 raised to the power 1/2. So any number, when multiplied by itself, produces its square, and when the square root of any squared number is taken, it produces the actual number.
Let us discuss each of them to understand the concepts better.
Square Root by Long Division Method
The process of long division is one of the most common methods used to find the square roots of a given number. It is easy to comprehend and provides more reliable and accurate answers. The long division method reduces a multi-digit number to its equal parts.
Learning how to find the square root of a number is easy with the long division method. All you need are five primary operations- divide, multiply, subtract, bring down or raise, then repeat.
Following are the simple steps that must be followed to find the square root of 256 using the long division method:
Step 1
First, write the given number 256 in the division symbol, as shown in figure 1.
Step 2
Starting from the right side of the number, divide the number 256 into pairs such as 56 and 2.
Step 3
Now divide the digit 2 by a number, giving a number either 1 or less than 1. Therefore, in this case, the remainder is 1 whereas the quotient is also 0ne.
Step 4
After this, bring down the next pair 56. Now the dividend is 56. To find the next divisor, we need to double our quotient obtained before. Doubling 1 gives 2; hence consider it as the next divisor.
Step 5
Now pair 2 with another number to make a new divisor that results in $\leq$ 156 when multiplied with the divisor.
Step 6
Adding 6 to the divisor and multiplying 26 with 6 results in 156 = 156. The remainder obtained is 0.
Step 7
The resulting quotient 16 is the square root of 256. Figure 1 given below shows the long division process in detail:
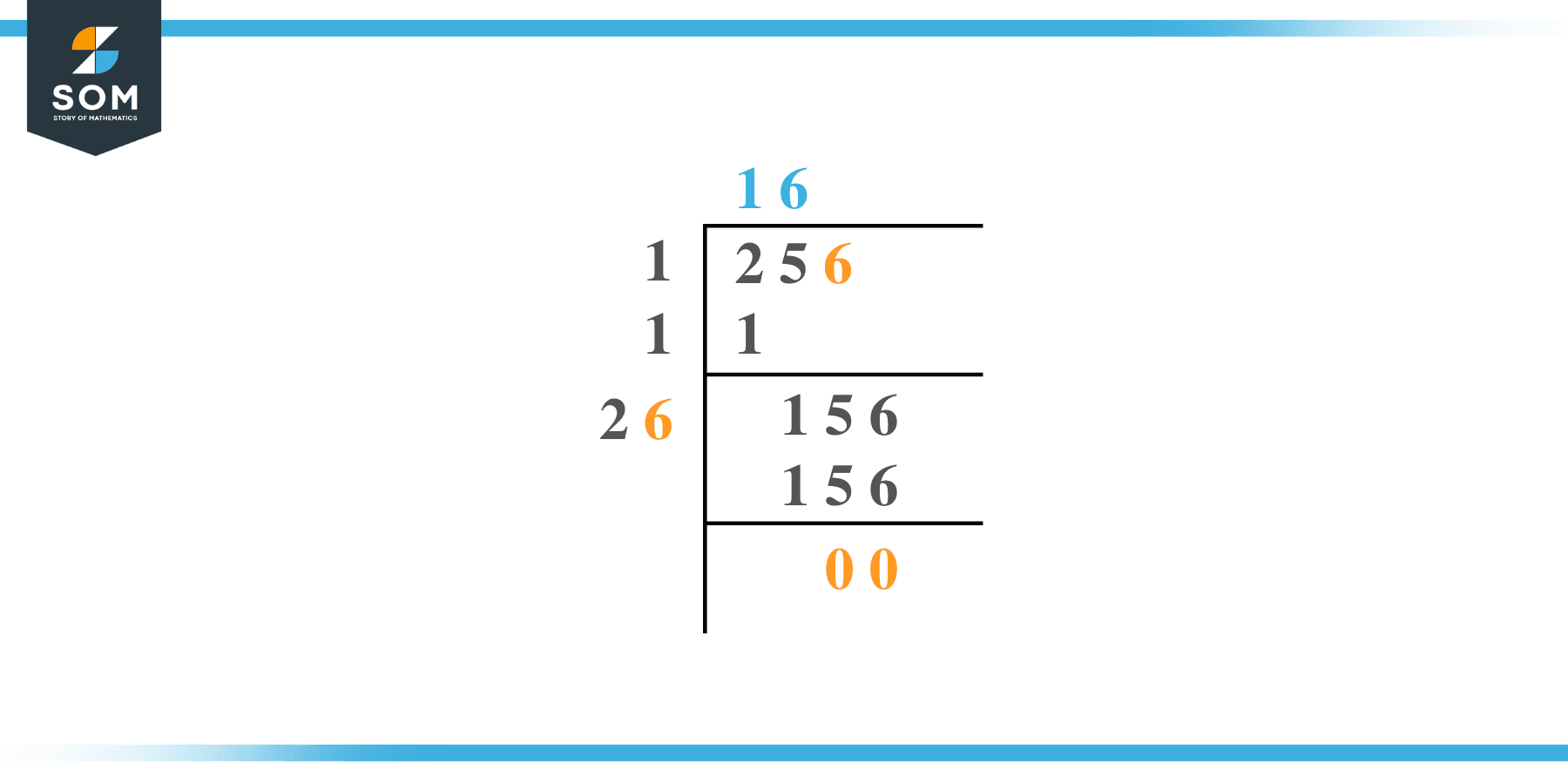
Figure 1
Important points
- The number 256 is a perfect square.
- The number 256 is a rational number.
- The number 256 can be split into its prime factorization.
Is Square Root of 256 a Perfect Square?
The number 256 is a perfect square. A number is a perfect square if it splits into two equal parts or identical whole numbers. If a number is a perfect square, it is also rational.
A number expressed in p/q form is called a rational number. All the natural numbers are rational. A square root of a perfect square is a whole number; therefore, a perfect square is a rational number.
A number that is not a perfect square is irrational as it is a decimal number. As far as 256 is concerned, it is a perfect square / not a perfect square. It can be proved as below:
Factorization of 256 results in 16 x 16 which can also be expressed as 16$^2$.
Taking the square root of the above expression gives:
= √(16$^2$)
= (16$^2$)$^{1/2}$
= 16
This shows that 256 is a perfect square and a rational number.
This shows that 256 is not a perfect square as it has decimal places; hence it is an irrational number.
Therefore the above discussion proves that the square root of 256 is equivalent to 16.
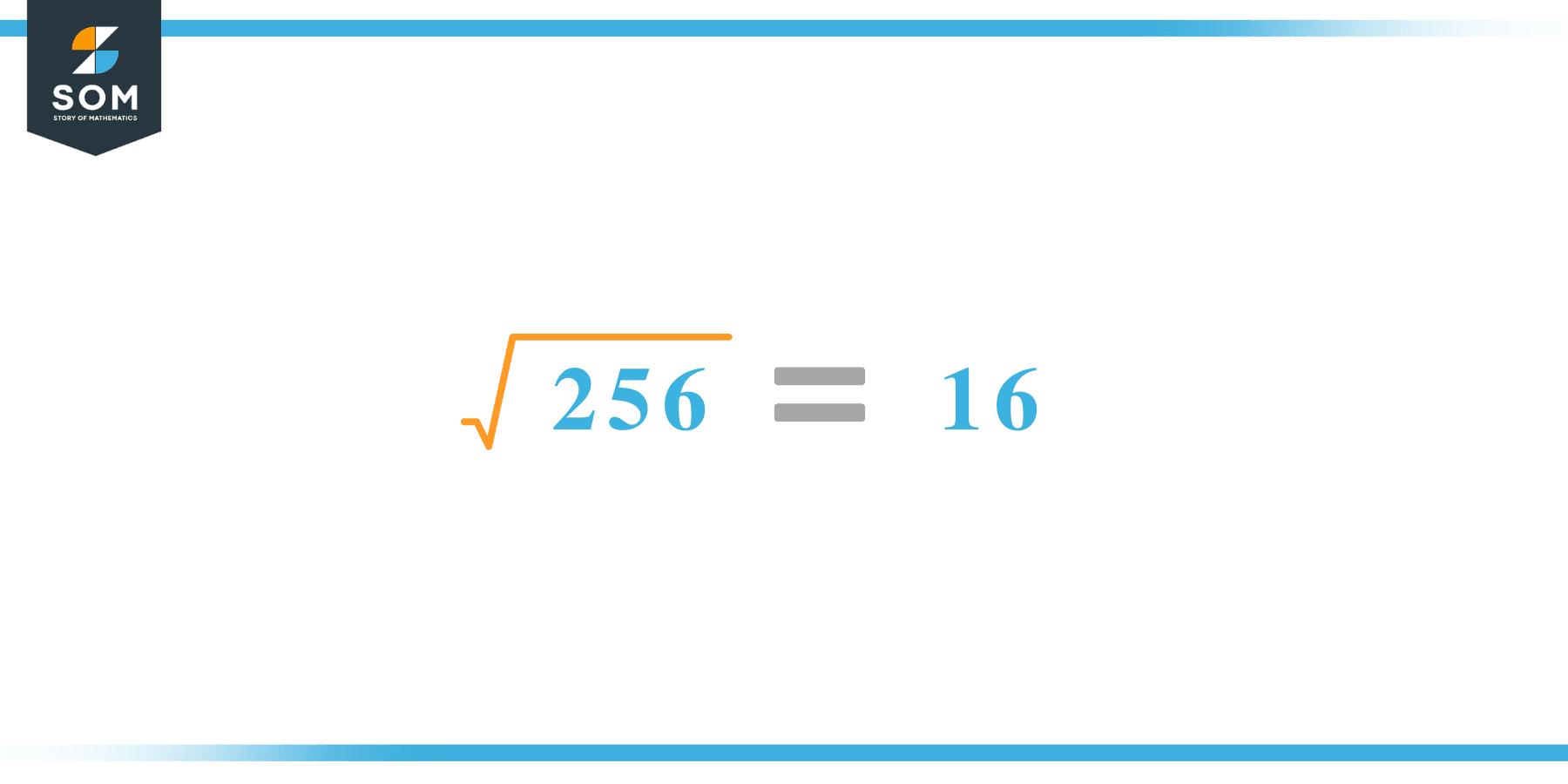
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
