JUMP TO TOPIC
Scalene Triangle|Definition & Meaning
Definition
A type of triangle in which none of the sides have the same length is called a scalene triangle. This results in all the angles being consequently unequal as well.
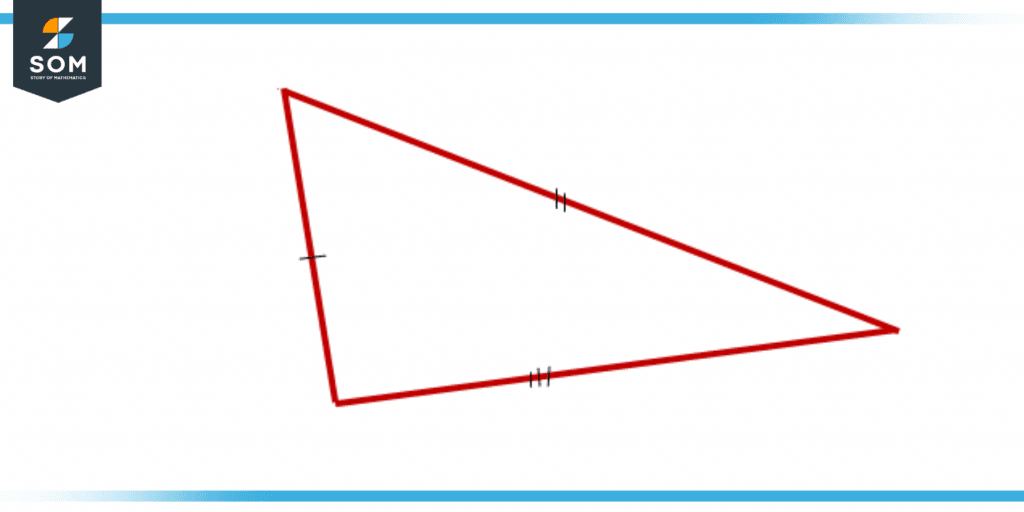
Figure 1 – Scalene Triangle
Scalene triangles can have any combination of side lengths as long as they do not form an equilateral triangle (with all sides equal). A scalene triangle is one where all three sides have variable lengths. In other words, if you pick any one of the three sides, it will not be equal to the other two.
Scalene triangles are a fundamental shape in mathematics and play an important role in many aspects of daily life. Whether they are used to calculate the area and perimeter of a triangle, prove mathematical theorems, or build structures, scalene triangles are versatile and useful shapes.
Further Explanation
Scalene triangles are unique in their dimensions and are different from isosceles and equilateral triangles. In an isosceles triangle, its two sides are equivalent in length and the third side is of a different length, while in an equilateral triangle, all three sides are equal.
Scalene triangles are important in mathematics because they are used in the calculation of the perimeter and area of the triangle. The area of the scalene triangle would be obtained by using Heron’s formula, which takes into account the length of the three sides and the semi-perimeter of the triangle. The perimeter of a scalene triangle is simply the addition of the sides.
Scalene triangles are also used in geometry to prove theorems and solve problems. For example, one theorem that can be proven using scalene triangles is the Pythagorean theorem, which would be stated as the square of the longest length side of a right triangle (the hypotenuse) is equal to the addition of the squares of its other two sides.
In addition to their mathematical importance, scalene triangles are also important in everyday life. They are used in construction, engineering, and design to build structures that are strong and stable. For example, scalene triangles can be used as support structures for bridges and buildings, as well as for creating frames for furniture and other objects.
Scalene triangles can also be found in nature, such as in the shapes of mountains, hills, and valleys. The different side lengths of scalene triangles can create diverse landscapes, with steep slopes and gradual inclines.
Types of Triangles Based on their Size and Shapes
There are four main types of triangles based on the length of their sides.
Equilateral Triangle
In an equilateral triangle, all three sides have an equal length. This means that all three sides are congruent, and all three angles are equal to 60°. Equilateral triangles are important in geometry because they can demonstrate the concept of congruence and symmetry. Since the interior angles are all equal to 60 degrees, this demonstrates the fact that the sum of a triangle’s interior angles is always 180°.
Isosceles Triangle
In an isosceles triangle, one side is of a different length, and the other two sides are of equal length. These two equal sides are the legs, and the third (uneuqal) side is the base of that triangle. The height of the triangle can be drawn from the base to the midpoint of the other two sides, forming two congruent right triangles. Isosceles triangles are important in mathematics because they can be utilized to find the area of the triangle by multiplying the base by the height and dividing by 2.
Scalene Triangle
As mentioned already, none of the sides have the same length in a scalene triangle. This means that all three sides are not congruent, and all three angles are different. Scalene triangles are important in geometry because they demonstrate the concept of non-congruence and can be used to demonstrate the fact that the summation of all the interior angles of a triangle is 180°.
Right Triangle
A right triangle is another type of triangle that has one right angle (90°) and two acute angles. The side which is opposite to the right angle is the hypotenuse and is always the longest side. Right triangles are important in mathematics as they are used to illustrate the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the longest side that is hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of its other two sides. Right triangles are also used in trigonometry to calculate the ratios of the side’s length, such as the sine, cosine, and tangent ratios.
Types of Scalene Triangle
Following are the different types of Scalene Triangles
Right Scalene Triangle
A right scalene triangle is a triangle with one right angle (90°). The other two angles are both acute, and all three sides have different lengths. The side which is opposite to the right angle is the hypotenuse and is always the longest side. Right scalene triangles are important in mathematics as they are used to illustrate the Pythagorean theorem states that the square of the length of the longest side is equal to the summation of the squares of its two other sides.
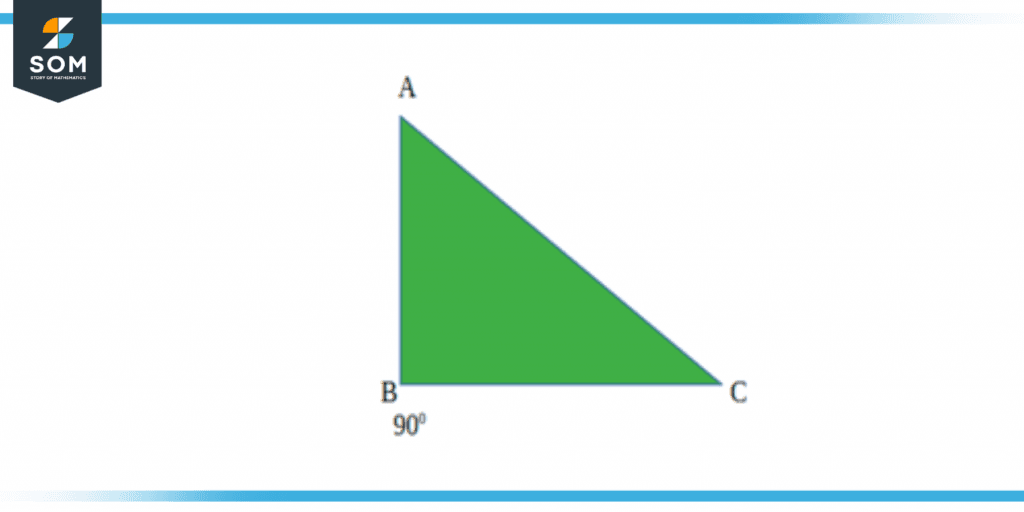
Figure 2 – Right Scalene Triangle
Obtuse Scalene Triangle
An obtuse scalene triangle is a triangle with one obtuse angle (greater than 90°). All three sides have different lengths, and the obtuse angle is always the largest angle in the triangle. Obtuse scalene triangles are important in geometry because they can be used to demonstrate that the summation of the angles in that triangle is always 180°.
Acute Scalene Triangle
An acute scalene triangle is a triangle with all angles less than 90°. The three sides have different lengths, and no side is longer than the sum of the other two sides. Acute scalene triangles are important in geometry because they can be used to demonstrate that the summation of the angles in the triangle is 180°.
Scalene Triangle With Equal Height
A scalene triangle with equal height is a triangle with three sides of different lengths but with the heights from the sides equal in length. The height is a line that is perpendicular to the base of the triangle and bisects it into equal halves. Scalene triangles with equal heights are important in geometry because they can be used to demonstrate that the area of a triangle is proportional to its height.
Scalene Triangle With Equal Medians
A scalene triangle with equal medians is a triangle with three sides of different lengths but with the medians (lines that bisect the triangle into equal halves) equal in length. Scalene triangles with equal medians are important in geometry because they can be used to demonstrate that the medians of a triangle always divide each other in a 2:1 ratio.
Scalene Triangles With Equal Areas
A scalene triangle is a triangle with an equal area and has three sides of variable lengths but with the area equal. This type of scalene triangle is important in geometry because it can be used to demonstrate that the area of a triangle is not dependent on the lengths of its sides.
Example of a Scalene Triangle Problem
Form a triangle with sides of length 5cm, 9cm, and 12cm.
Solution
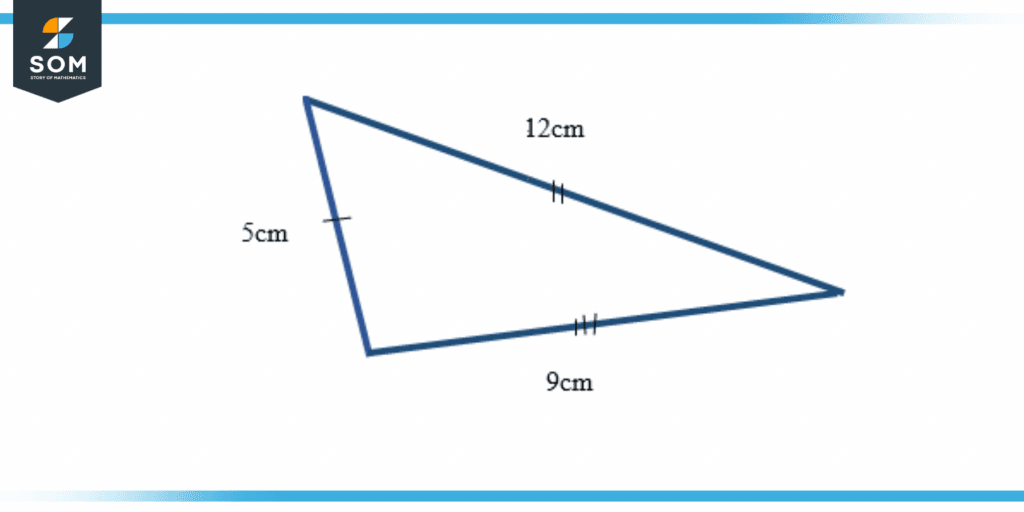
Figure 3 – Scalene Triangle Example
The figure above is a triangle with three different sides which is a scalene triangle.
All the figures above were created on GeoGebra.
