- Home
- >
- Place Value – Explanation & Examples
Place Value – Explanation & Examples
 What is a Place Value?
What is a Place Value?
In mathematics, every integer in a number has a place value. Therefore, the place value of a number is the value represented by a digit in a number based on its position in the number.
While a place value is the value a digit holds to be at the place in the number, on the other hand, the face value of a digit for any place in the given number is the value of the integer itself.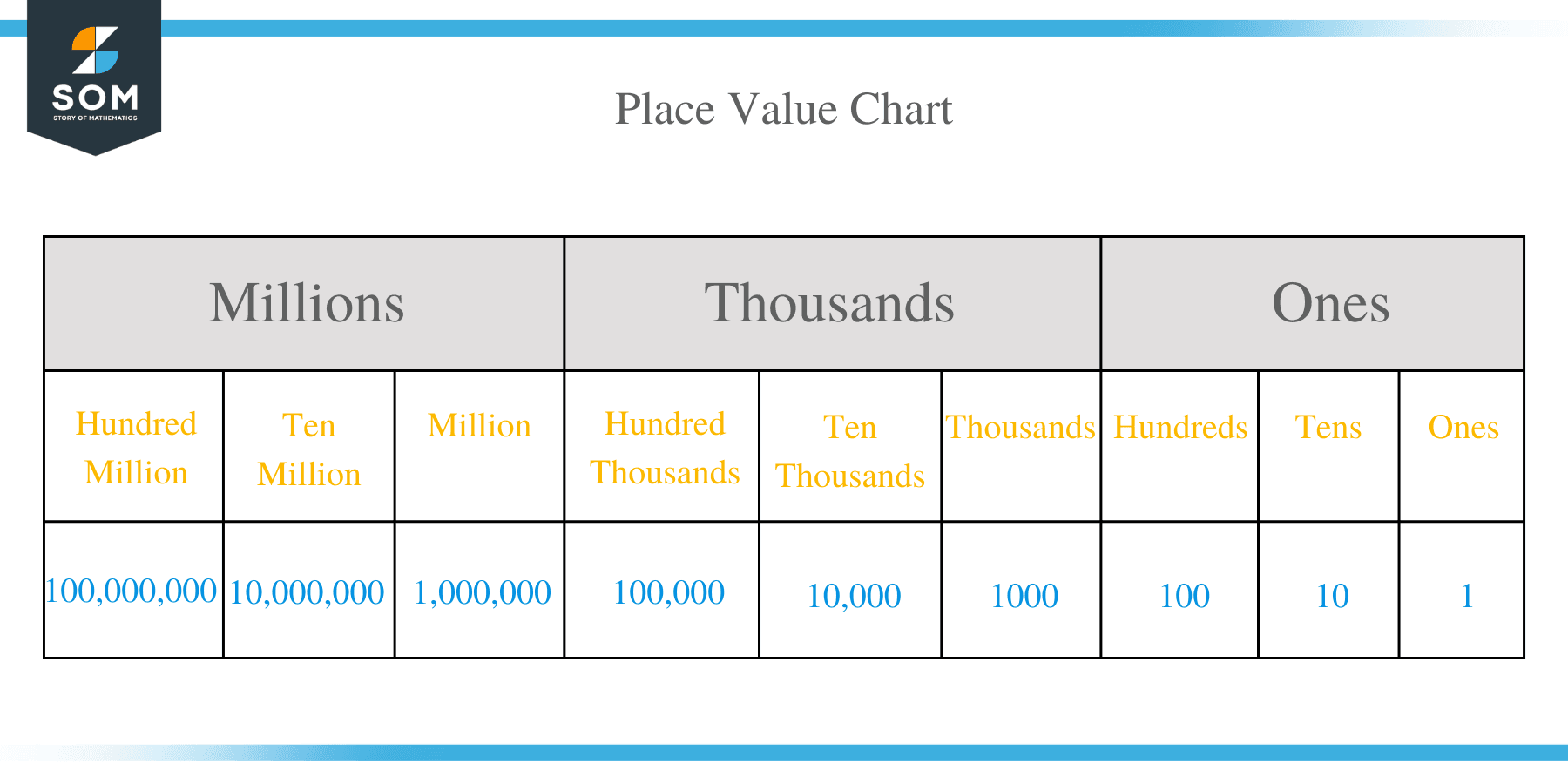
A place value chart is a diagram that helps us to find and compare the place value of the digits in numbers through millions. The place value of a digit in the place value chart increases by ten times as we shift to the left and decreases by ten times as we shift to the right.
| PLACE VALUE CHART |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
1 0 0 0 0 0 | 1 0 0 0 0 | 1 0 0 0 | 1 0 0 | 1 0 | 1 | Decimal point | 0 . 1 | 0 . 0 1 | 0 . 0 0 1 | 0 . 0 0 0 1 | 0 . 0 0 0 0 1 | 0 . 0 0 0 0 0 1 | ||
| 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 5 |
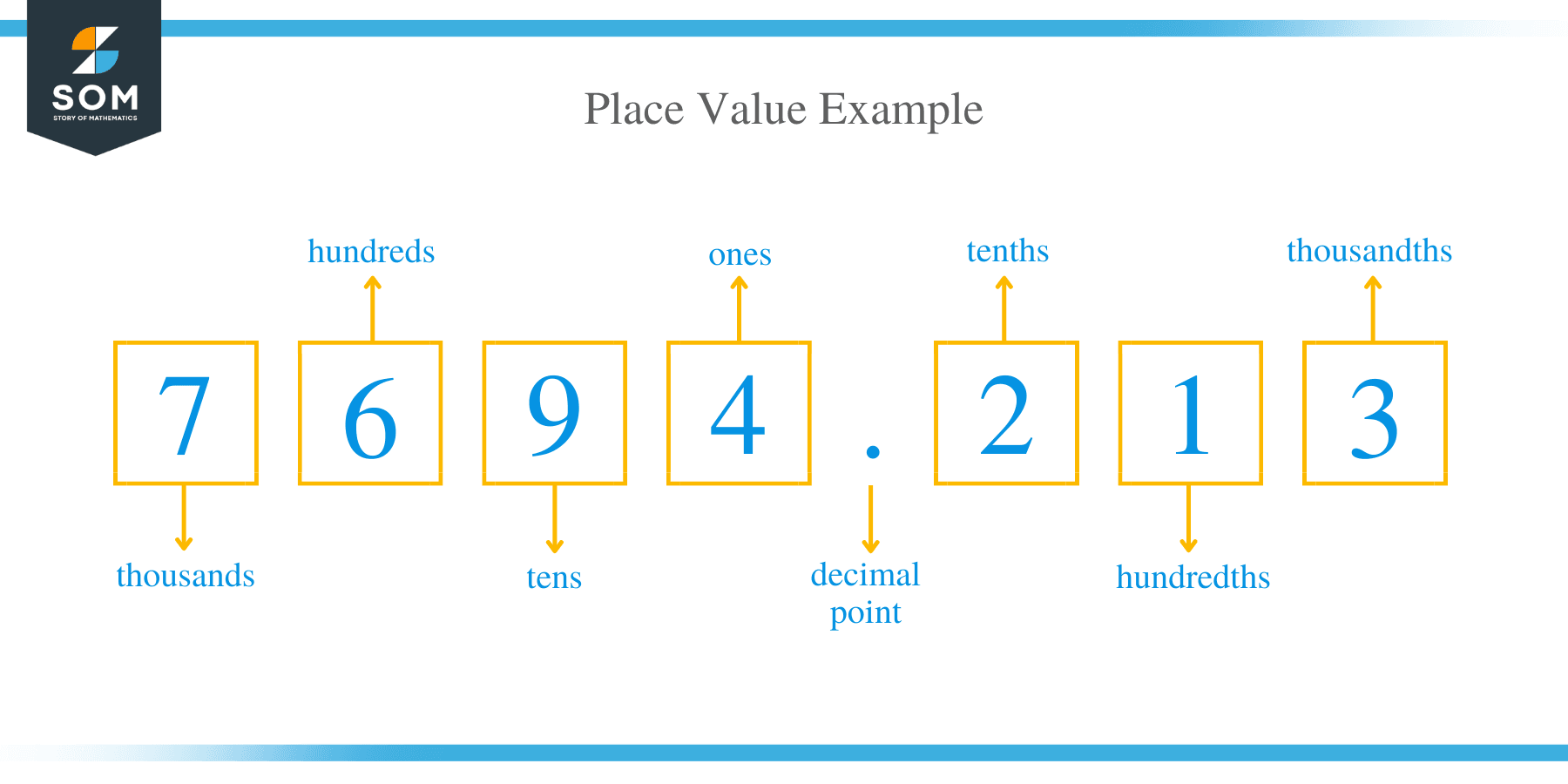
Example 1
Consider a number: 24.3185
- The digit 2 is in the tens place, and it has a value of 2 × 10 = 20
- The digit 4 is in the one’s place, and it has the value of 4 × 1 = 4
- The digit 3 is in the tenths place, and it has a value of 3 × 1/10 = 3/10 = 0.3
- The digit 1 is in the hundredths place, and it has a value of 1 × 1/100 = 1/100 = 0.01
- The digit 8 is in the thousandths place, and it has a value of 8 × 1000 = 8/1000 = 0.008
- The digit 5 is in the ten-thousandths place, and it has a value of 5 × 10000 = 5/10000 = 0.0005
Therefore, the place value of a number is found by multiplying the face value and the value of the number itself
The place value for a one-digit number is equivalent to its face value. For instance, the place value and face value of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9, respectively.
The place value of zero in any number is always zero. Zero may hold any place in a number, but its value will remain to be zero.
Example 2
In numbers having zeros such as 105, 350, 42017, 90218, the place value of 0 in each number is 0.
For a two-digit number, the place value tens digit is 10 times the digit, For example, the place value of 5 in number 57 is 5 x 10 = 50, and the place value of the one-digit is 7 x 1 =7.
Similarly, hundreds of digits’ place value in a three-digit number is 100 x the digit’s face value. For example, the place value of 4 in the number 475 is 4 x 100 = 400.
Thus, for a digit’s place value, the digit is multiplied by the place value of 1; it has to be that place. The methods of finding and writing the place value of any digit in a number are illustrated below with different examples.
Example 3
Write down the place value of each digit in the number: 768;
- The place value of 8 = 8 × 1 = 8
- The place value of 6 = 6 × 10 = 60
- The place value of 7 is 7 × 100 = 700.
We can summarize that a number holds its place value as the product of the number and place value of one to be at that position.
Example 4
Find the place value of all digits in the number: 4129.
- The place value of 9 is 9 × 1 = 9
- The place value of 2 is 2 × 10 = 20
- The place value of 1 is 1 × 100 = 100
- The place value of 4 is 4 × 1000 = 4000
Example 5
Write down the place value of the digits in 2965.
- The digit 2 is at the thousand’s place; therefore, its place is 1000 x 2 = 2000
- The digit 9 is the hundred’s place, and so, the place value is 9 x 100 = 900
- The number 6 is at the ten’s place, so, the place value of 6 = 6 x 10 = 60
- The number 5 occupies the one’s place in the number 2965; therefore, the place value of 5 is 5 x 1 = 5
Example 6
Write down the place of the digits in the following number: 9721.
- The number 9 is at a thousand’s place in 9721. So, the place value of 9 is 9 x 1000 = 9000.
- Another number 7 is at hundred’s place in 9721. Therefore, the place of 7 is equal to 7 x 100 = 700.
- The number 2 is at the ten’s place. So, the place of 2 in the number 9721 is equal to 2 x 10 = 20.
- The number 1 occupies the place of ones. And for this case, its place value is 1 x 1 =1.
