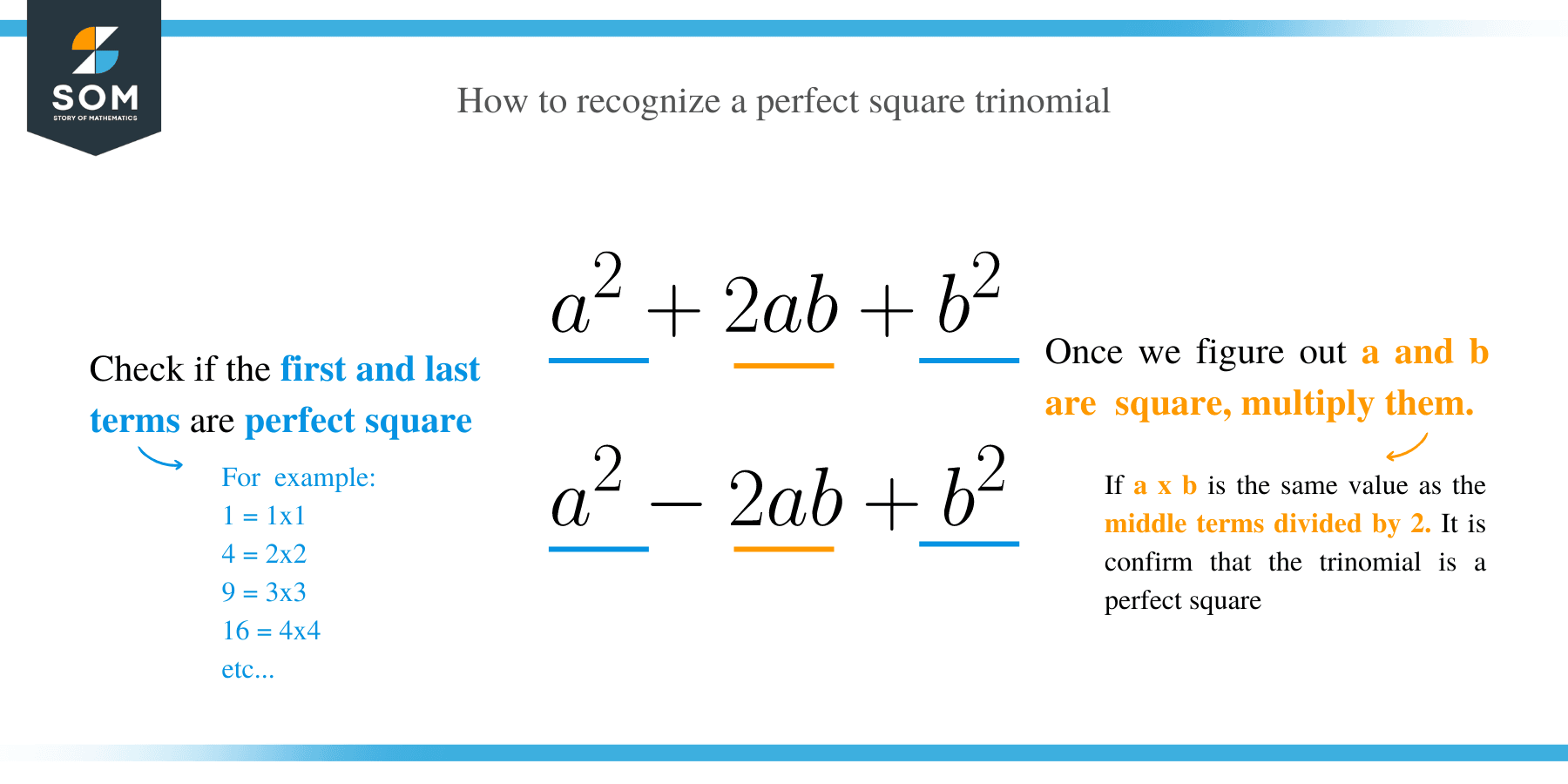- Home
- >
- Perfect Square Trinomial – Explanation & Examples
JUMP TO TOPIC
Perfect Square Trinomial – Explanation & Examples
 A quadratic equation is a second degree polynomial usually in the form of f(x) = ax2 + bx + c where a, b, c, ∈ R, and a ≠ 0. The term ‘a’ is referred to as the leading coefficient, while ‘c’ is the absolute term of f (x).
A quadratic equation is a second degree polynomial usually in the form of f(x) = ax2 + bx + c where a, b, c, ∈ R, and a ≠ 0. The term ‘a’ is referred to as the leading coefficient, while ‘c’ is the absolute term of f (x).
Every quadratic equation has two values of the unknown variable, usually known as the roots of the equation (α, β). We can obtain the roots of a quadratic equation by factoring the equation.
What is a Perfect Square Trinomial?
The ability to recognize special cases of polynomials that we can easily factor in is a fundamental skill for solving any algebraic expressions that involve polynomials.
One of these “easy to factor” polynomials is the perfect square trinomial. We can recall that a trinomial is an algebraic expression composed of three terms connected by addition or subtraction.
Similarly, a binomial is an expression composed of two terms. Therefore, a perfect square trinomial can be defined as an expression that is obtained by squaring a binomial
Learning how to recognize a perfect square trinomial is the first step to factoring it.
The following are the tips on how to recognize a perfect square trinomial:
- Check whether the first and last terms of the trinomial are perfect squares.
- Multiply the roots of the first and third terms together.
- Compare to the middle terms with the result in step two
- If the first and last terms are perfect squares, and the middle term’s coefficient is twice the product of the square roots of the first and last terms, then the expression is a perfect square trinomial.
How to Factor a Perfect Square Trinomial?
Once you have identified a perfect square trinomial, factoring it is quite a straightforward process.
Let’s take a look at the steps for factoring a perfect square trinomial.
- Identify the squared numbers in the first and third terms of the trinomial.
- Examine the middle term if it has either positive or negative. If the middle term of the trinomial is positive or negative, then the factors will have a plus and minus sign, respectively.
- Write out your terms by applying the following identities:
(i) a2 + 2ab + b2 = (a + b)2 = (a + b) (a + b)
(ii) a2 – 2ab + b2 = (a – b)2 = (a – b) (a – b)
Perfect Square Trinomial Formula
An expression obtained from the square of a binomial equation is a perfect square trinomial. An expression is said to a perfect square trinomial if it takes the form ax2 + bx + c and satisfies the condition b2 = 4ac.
The perfect square formula takes the following forms:
- (ax)2 + 2abx + b2 = (ax + b)2
- (ax)2 −2abx + b2 = (ax−b)2
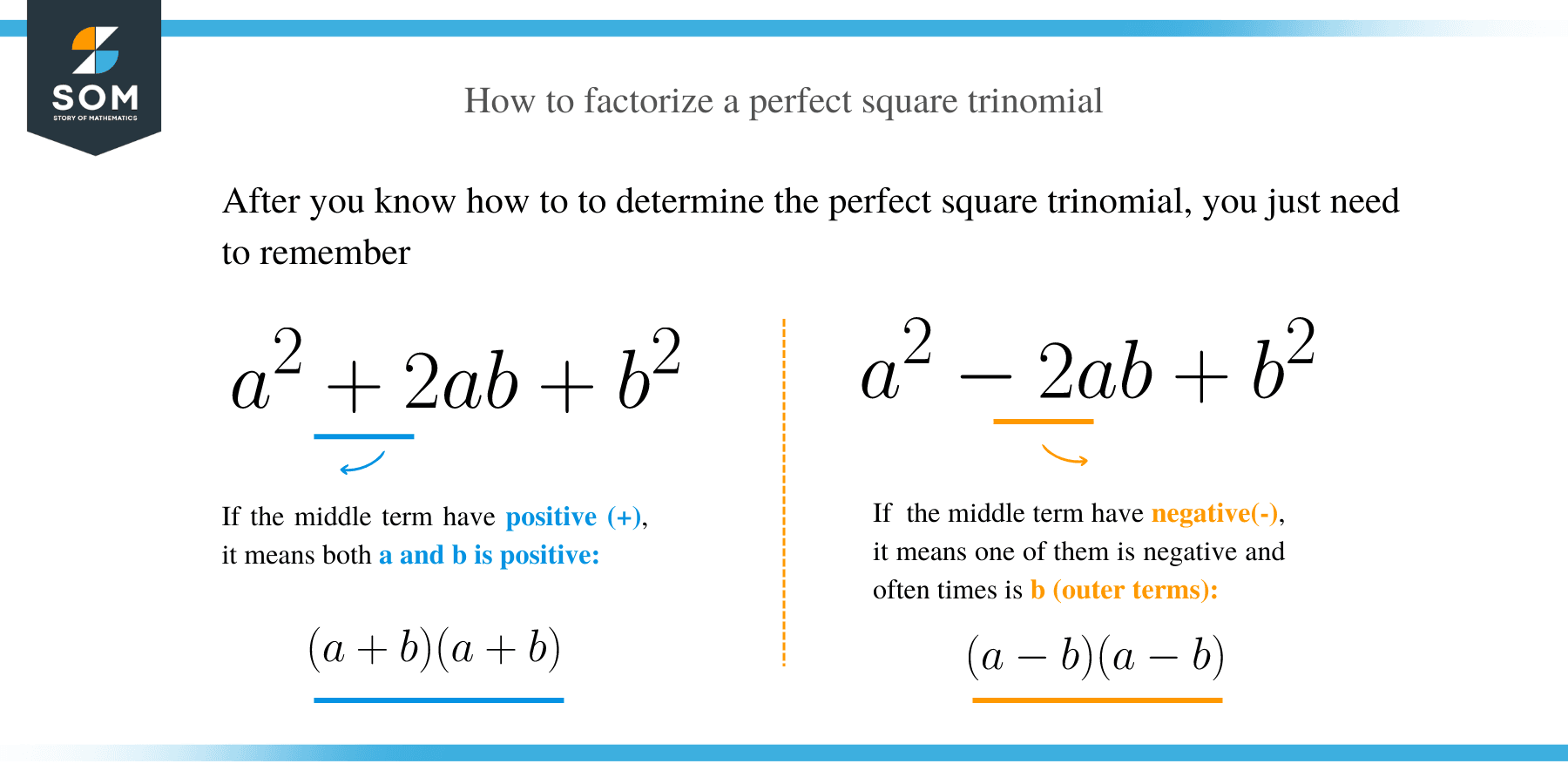
Example 1
Factor x2+ 6x + 9
Solution
We can rewrite the expression x2 + 6x + 9 in the form a2 + 2ab + b2 as;
x2+ 6x + 9 ⟹ (x)2 + 2 (x) (3) + (3)2
Applying the formula of a2 + 2ab + b2 = (a + b)2 to the expression gives;
= (x + 3)2
= (x + 3) (x + 3)
Example 2
Factor x2 + 8x + 16
Solution
Write the expression x2 + 8x + 16 as a2 + 2ab + b2
x2 + 8x + 16 ⟹ (x)2 + 2 (x) (4) + (4)2
Now we will apply the perfect square trinomial formula;
= (x + 4)2
= (x + 4) (x + 4)
Example 3
Factor 4a2 – 4ab + b2
Solution
4a2 – 4ab + b2 ⟹ (2a)2 – (2)(2) ab + b2
= (2a – b)2
= (2a – b) (2a – b)
Example 4
Factor 1- 2xy- (x2 + y2)
Solution
1- 2xy- (x2 + y2)
= 1 – 2xy – x2 – y2
= 1 – (x2 + 2xy + y2)
= 1 – (x + y )2
= (1)2 – (x + y)2
= [1 + (x + y)] [1 – (x + y)]
= [1 + x + y] [1 – x – y]
Example 5
Factor 25y2 – 10y + 1
Solution
25y2 – 10y + 1⟹ (5y)2 – (2)(5)(y)(1) + 12
= (5y – 1)2
= (5y– 1) (5y – 1)
Example 6
Factor 25t2 + 5t/2 + 1/16.
Solution
25t2 + 5t/2 + 1/16 ⟹ (5t)2 + (2)(5)(t) (1/4) + (1/4)2
= (5t + 1/4)2
= (5t + 1/4) (5t + 1/4)
Example 7
Factor x4 – 10x2y2 + 25y4
Solution
x4 – 10x2y2 + 25y4 ⟹ (x2)2 – 2 (x2) (5y2) + (5y2)2
Apply the formula a2 + 2ab + b2 = (a + b)2 to get,
= (x2 – 5y2)2
= (x2 – 5y2) (x2 – 5y2)