- Home
- >
- Identity Property – Explanation with Examples
JUMP TO TOPIC
Identity Property – Explanation with Examples
 What is Identity Property?
What is Identity Property?
Real numbers are an ordered set of numbers that possess unique properties. The basic properties are commutative, associative, distributive, and identity. An identity property is a property that applies to a group of numbers in the form of a set. It cannot be applied to any individual number only.
It is named identity property because when applied to a number, the number keeps its ‘identity.’ The identity property is true for all arithmetic operations.
Identity Property of Addition
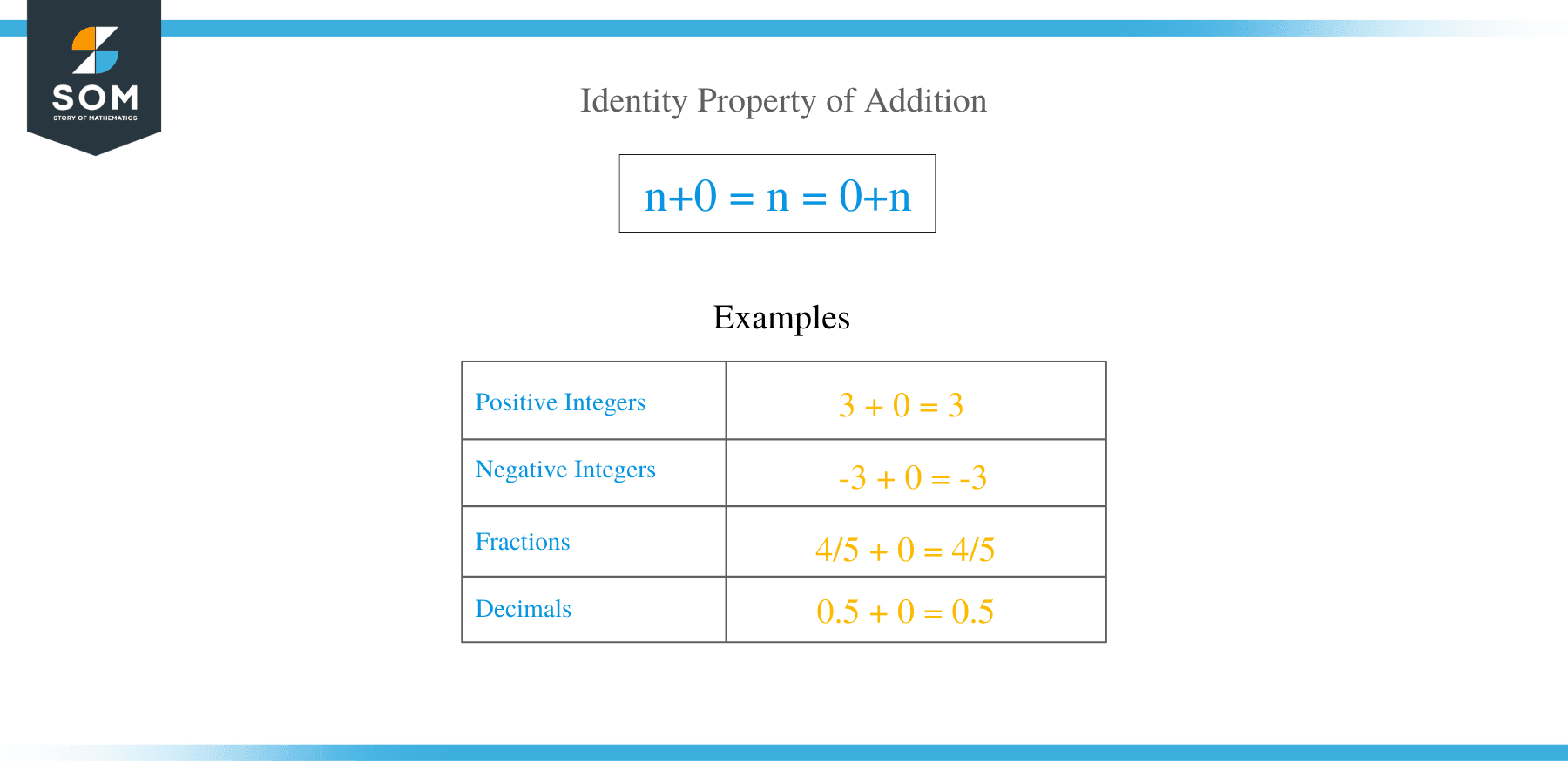 The identity property of addition is that when a number n is added to zero, the result is the number itself i.e.
The identity property of addition is that when a number n is added to zero, the result is the number itself i.e.
n + 0 = n
Zero is called an additive identity and it can be added to any real number without changing its value. Here are the few examples of identity property of addition,
3 + 0 = 3 (Positive Integers)
-3 + 0 = -3 (Negative Integers)
4/5 + 0 = 4/5 (Fractions)
0.5 + 0 = 0.5 (Decimals)
x + 0 = x (Algebraic notation)
This property holds true for subtraction as well because subtracting 0 from any number equals the number itself. Therefore, 0 is also called a subtractive identity.
Identity Property of Multiplication
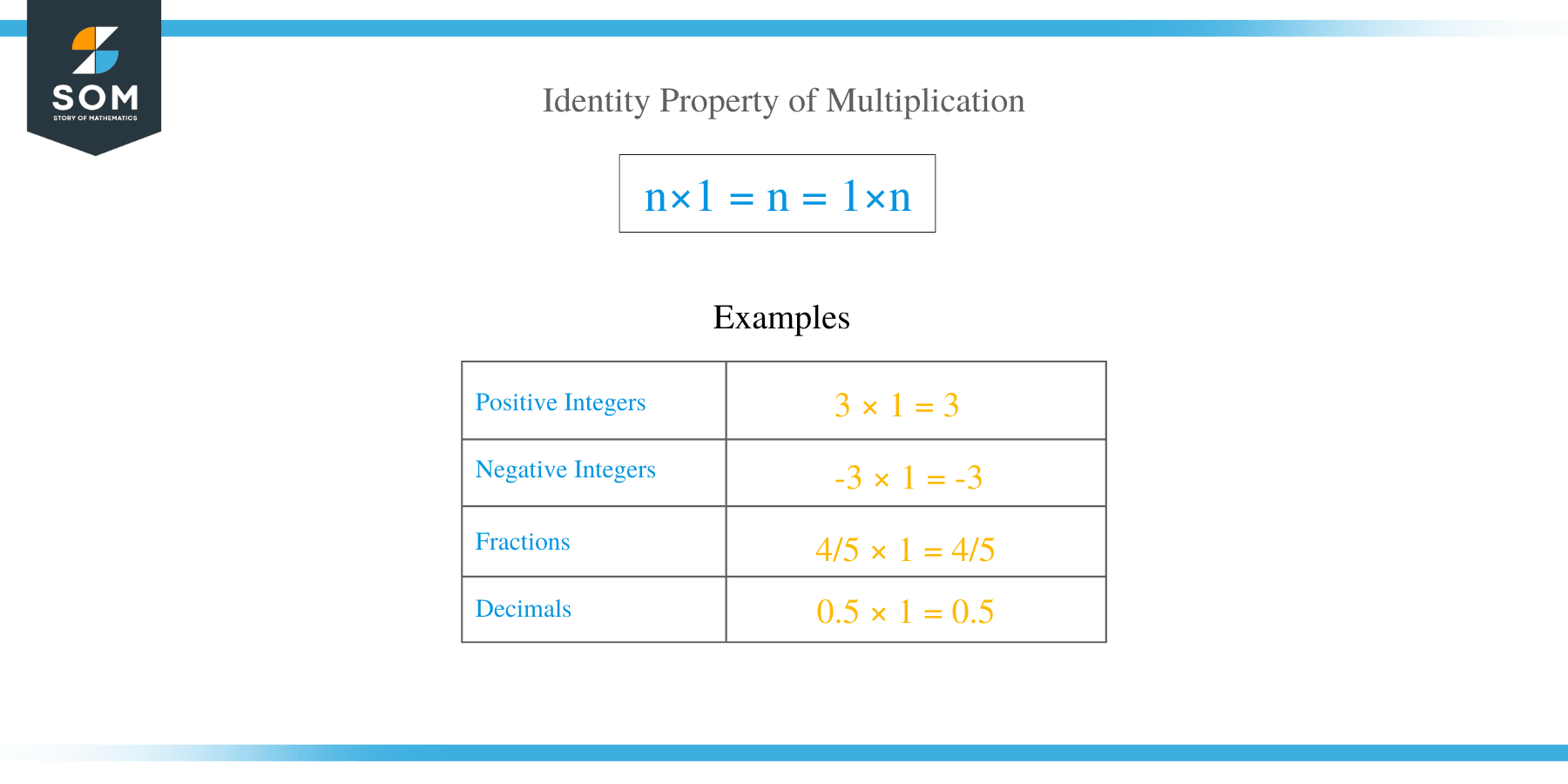 The identity property of multiplication is that when a number n is multiplied by one, the result is the number itself i.e.
The identity property of multiplication is that when a number n is multiplied by one, the result is the number itself i.e.
n × 1 = n
One is called the multiplicative identity, and it can be multiplied with any real number without changing its value. Here are a few examples of identity property of multiplication,
3 × 1 = 3 (Positive Integers)
-3 × 1 = -3 (Negative Integers)
4/5 × 1 = 4/5 (Fractions)
0.5 × 1 = 0.5 (Decimals)
x × 1 = x (Algebraic notation)
This property holds true for division as well because dividing any number by 1 equals the number itself. Therefore, 1 is also called divisive identity.
