JUMP TO TOPIC
Oblique Cylinder|Definition & Meaning
Definition
A cylinder that “leans over” or has sides that aren’t parallel to the bases is an oblique cylinder.
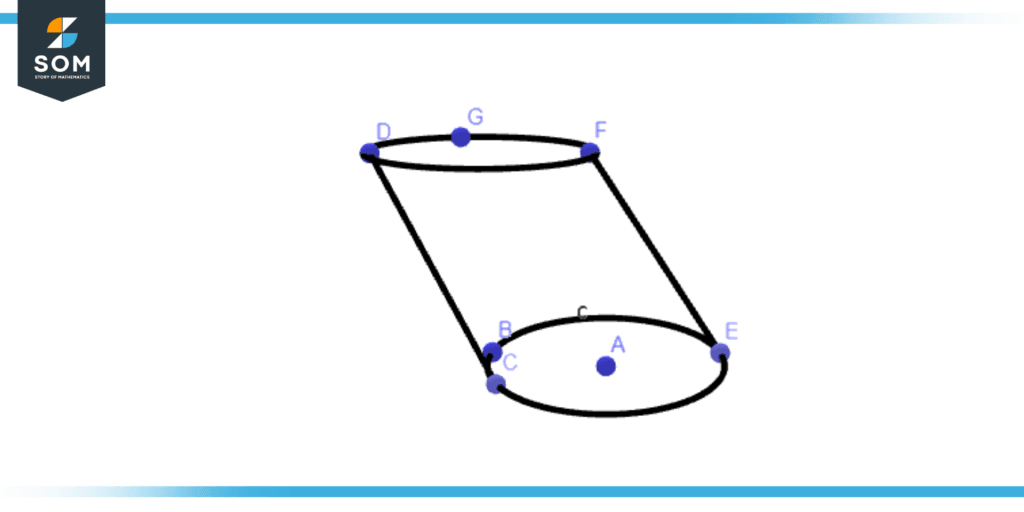
Figure 1 – Oblique cylinder
Figure 1 illustrates an oblique cylinder. It is a three-dimensional object with two straight sides connecting its top and bottom circular bases. Oblique cylinders are those whose sides are inclined rather than parallel to their bases. The top base is not precisely above the bottom base because of the cylinder’s slant to one side.
Difference Between Right Cylinder and Oblique Cylinder
A cylinder is referred to be a right circular cylinder if the segments connecting the circular bases’ centers are perpendicular to their two planes. An oblique circular cylinder is one where the segments connecting the centers of the circles are not parallel to the planes of the circles. Figure 2 illustrates the graphical view of the right cylinder and oblique cylinder.
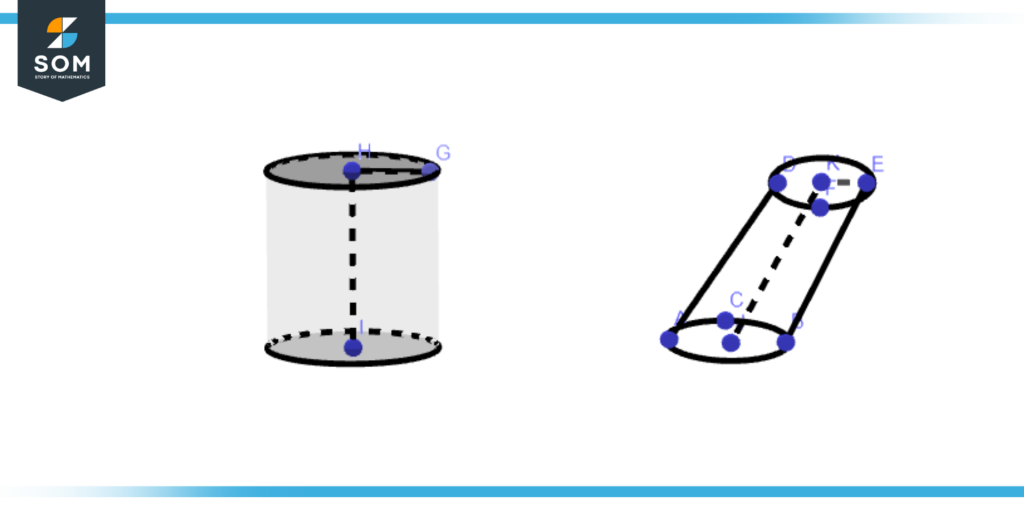
Figure 2 – Difference between right cylinder and oblique cylinder
Volume of an Oblique Cylinder
The area occupied by an oblique cylinder in a three-dimensional plane is called its volume. It is the same as a right cylinder of the same height. Its dimensions are expressed in cubic units like cubic meters,cubic centimeters, cubic millimeters, and cubic feet, much like a right cylinder. Figure 3 illustrates the graphical view of the volume of an oblique cylinder.
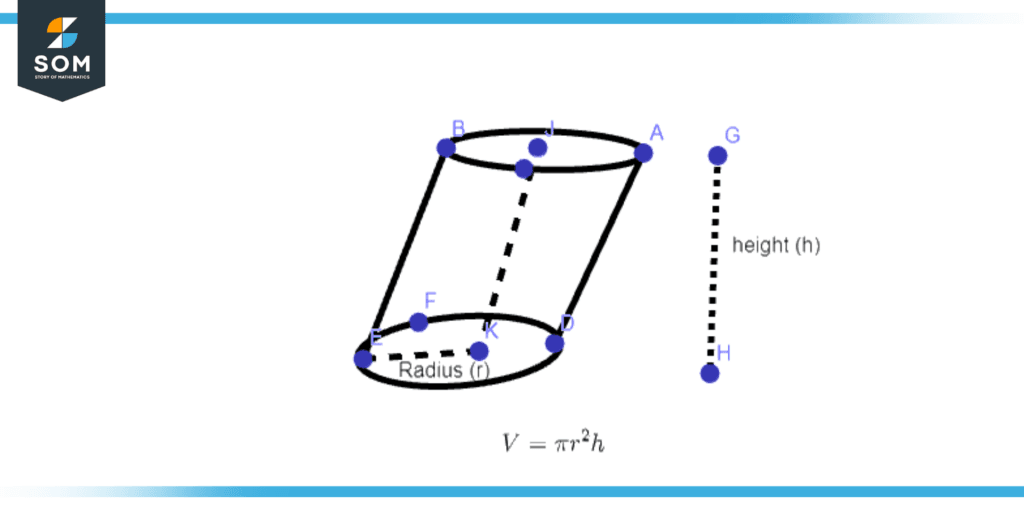
Figure 3 – Volume of an Oblique Cylinder
Curved Surface Area of an Oblique Cylinder
The region created by a cylinder’s curved surface is known as the lateral or curved surface area (LSA). Therefore, it is the area that is occupied by the two parallel circular bases. The curved surface area of an oblique cylinder is calculated using the formula:
Curved Surface Area (CSA) = 2$\pi$RL
where L is the length of one of the slanted sides and R is the radius of the circle.
Total Surface Area of an Oblique Cylinder
The area that the full oblique cylinder occupies is known as its total surface area (TSA). It covers the space occupied by two round bases and one curved surface. The formula for the total Surface area of an oblique cylinder is given below:
Total surface area (TSA) = L + 2$\pi$R2
Again, L is the length of one of the slanted sides, and R is the radius of the circle.
Examples of Oblique Cylinder
Example 1
a) If the height of the oblique cylinder is 24 inches and the diameter of the cylinder is 22 inches. Find the volume of an oblique cylinder.
b) The radius of an oblique cylinder is equal to 4 cm, and the length of the cylinder is 10cm. Find the curved surface area of the oblique cylinder.
c) Find the volume of an oblique cylinder if the height of the cylinder is 5 cm and the volume of the cylinder is 25 cubic cm.
Solution
a) As we know, the volume of an oblique cylinder is:
Volume=$\pi$r2h
As we have the diameter of the cylinder so the radius will be equal to $\mathsf{\dfrac{22}{2}} = 11$.
So the volume of the cylinder is equal to:
Volume = (3.412)(11)(11)(24)
Volume = 9121.464 cubic inches
b) The formula for the curved surface area is:
Curved Surface Area (CSA) = 2$\pi$rl
Curved Surface Area (CSA) = 2(3.142) (4)(10)
Curved Surface Area (CSA) = 251.36 sq cm
c) As we know that:
Volume = $\pi$r2h
The volume of the cylinder is given as 25 cubic cm, while the height of the cylinder is given as 5 cm.
25 = 3.412 $\times$ r2 $\times$ 5
$\mathsf{\dfrac{25}{5}}$ = 3.1412 $\times$ r2
$\mathsf{\dfrac{5}{3.141}}$ = r2
r2 = 1.59
r = 1.26 cm
The radius of the given cylinder is equal to 1.26 cm.
Example 2
a) If the height of the oblique cylinder is 20 inches and the diameter of the cylinder is 10 inches. Find the volume of an oblique cylinder.
b) The radius of an oblique cylinder is equal to 10 cm, and the length of the cylinder is 20cm. Find the curved surface area of the oblique cylinder.
Solution
a) As we know, the volume of an oblique cylinder is:
Volume = $\pi$r2h
As we have the diameter of the cylinder so the radius will be equal to $\mathsf{\dfrac{10}{2}} = 5$.
So the volume of the cylinder is equal to:
Volume = (3.412)(5)(5)(20)
Volume = 1570.6 cubic inches
b) The formula for the curved surface area is:
Curved Surface Area (CSA) = 2$\pi$rl
Curved Surface Area (CSA) = 2(3.142)(10)(20)
Curved Surface Area (CSA) = 1256.48 sq cm
Example 3
a) Find the volume of an oblique cylinder if the height of the cylinder is 5 cubic cm and the volume of the cylinder is 30 cubic cm.
b) Find the total surface area of an oblique cylinder if the radius of the cylinder is equal to 25 cm and the length of the cylinder is 15 cm.
Solution
a) As we know that:
Volume = $\pi$r2h
The volume of the cylinder is given as 30 cubic cm, while the height of the cylinder is given as 5 cm.
30 = 3.1412 $\times$ r2 $\times$ 5
$\mathsf{\dfrac{30}{5}}$= 3.1412 $\times$ r2
$\mathsf{\dfrac{6}{3.141}}$ = r2
r2 = 1.91
r = 1.34 cm
The radius of the given cylinder is equal to 1.34 cm.
b) As we know, the formula for the total surface area of the cylinder:
TSA = l + 2$\pi$r2
The length of the cylinder is given as 15 cm, and the radius of the cylinder is 25 cm, so:
Total surface area (TSA) = 15 + 2(3.142)(25)(25)
Total surface area (TSA) = 15 + 2(3.142)(625)
Total surface area (TSA) = 15 + 3927.5
Total surface area (TSA) = 3942.5 sq cm
So the total surface area of an oblique cylinder, according to the given data, is equal to 3942.5 sq cm.
Example 4
Find the length of an oblique cylinder if the radius of the cylinder is equal to 25 cm and the surface area of the cylinder is 4200 sq cm.
Solution
As we know, the formula for the total surface area of the cylinder:
TSA = l + 2$\pi$r2
The length of the cylinder is given as 15 cm, and the radius of the cylinder is 25 cm, so:
Total surface area (TSA) = 15 + 2(3.142)(25)(25)
4200 = l + 2(3.142)(625)
4200 – 3927.5 = l
Length of an oblique cylinder = 272.5 cm
So the length of the cylinder is equal to 272.5 cm if the total surface area is equal to 4200 sq cm.
All images were created using GeoGebra.
