JUMP TO TOPIC
Numerator|Definition & Meaning
Definition
A numerator is the part of a fraction that is located above the fraction line. It represents the number of parts of a whole that are being considered or referred to. For example, in the fraction “3/4,” the numerator is 3, which represents three parts of the whole.
The fraction line separates the two parts of the fraction, with the numerator above the line and the denominator below the line.
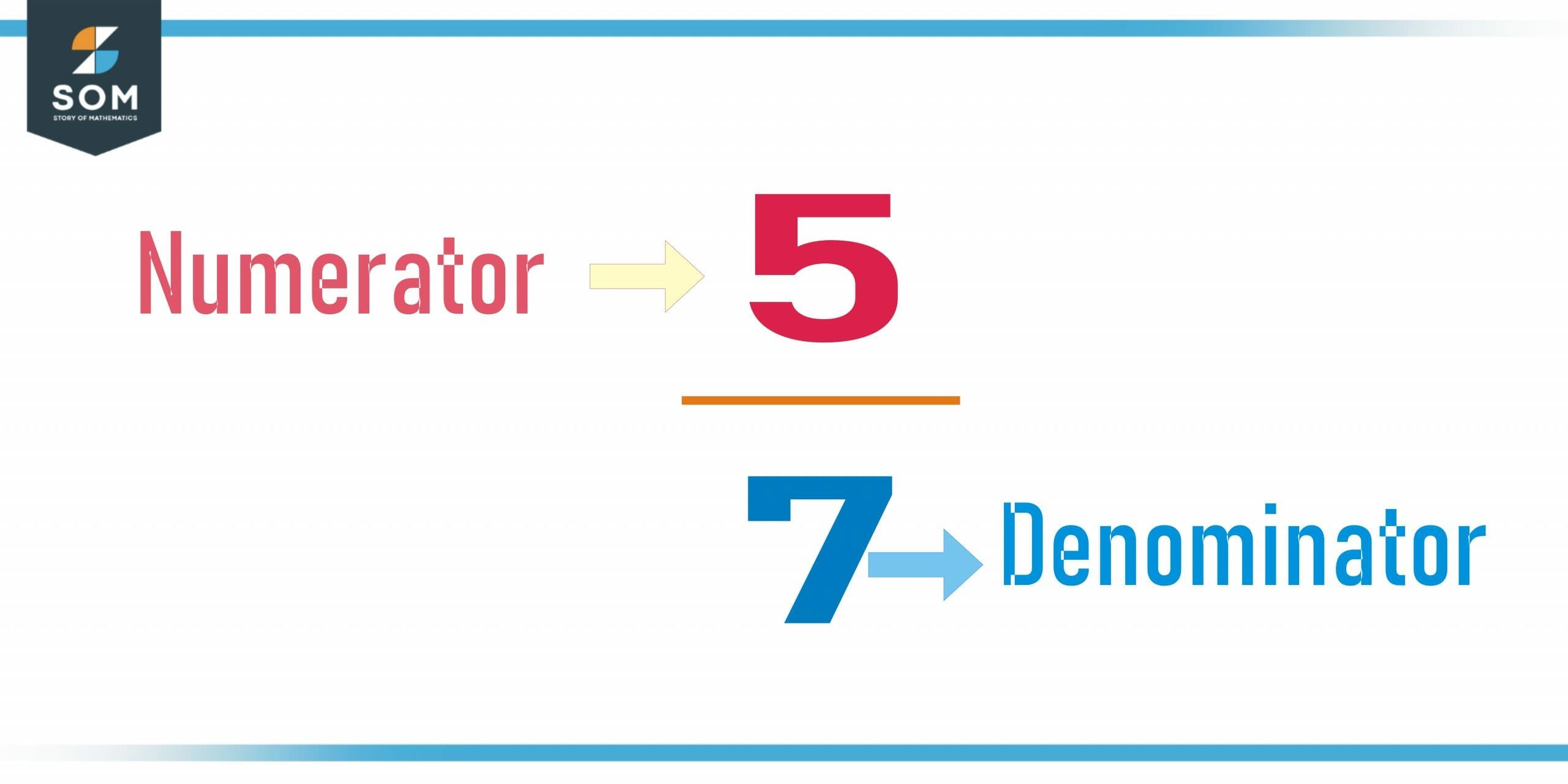
The numerator and denominator of a fraction are used to express a division problem. For example, the fraction 2/3 can be written as 2 divided by 3, or 2 ÷ 3. The numerator represents the number of parts being considered, and the denominator represents the number of parts into which each part is being divided. In this case, 2 parts are being considered, and each part is being divided into 3 smaller parts.
What Is the Denominator?
The denominator, which is located below the fraction line, represents the total number of parts that make up the whole. In the fraction “3/4,” the denominator is 4, which represents the total number of parts that make up the whole.
Fractions
Fractions are used to represent quantities that are not whole numbers. They are commonly used in mathematics to represent ratios and proportions. For example, if a pizza is cut into 8 slices and 3 of those slices are eaten, the fraction “3/8” could be used to represent the remaining amount of pizza.
Fractions can also be used to represent decimals, which are numbers that have a decimal point. A decimal can be converted into a fraction by dividing the number to the right of the decimal point by a power of 10. For example, the decimal “0.75” can be converted into the fraction “3/4” by dividing the number 75 by 100, which is the same as multiplying the fraction by 1.
Fractions can be simplified by dividing the numerator and denominator by a common factor. For example, the fraction “6/8” can be simplified to “3/4” by dividing both the numerator and denominator by 2. Simplifying fractions can make them easier to work with and understand.
Fractions can be compared by first finding a common denominator and then comparing the numerators. For example, to compare the fractions 1/3 and 2/4, we first find a common denominator by multiplying the denominators 3 and 4, which gives us a denominator of 12.
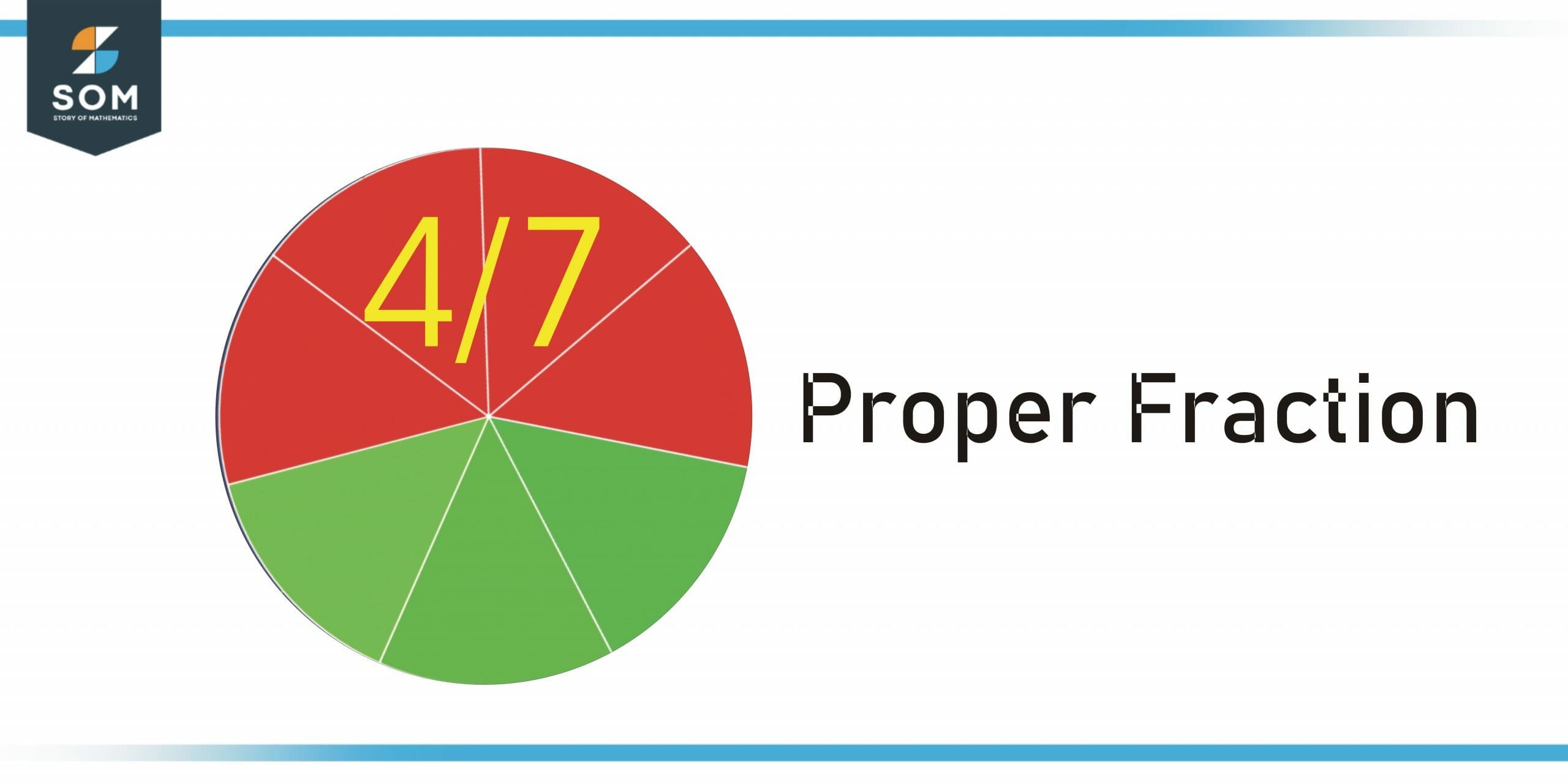
Figure 2 – Proper Fraction with numerator 4 and denominator 7
We then rewrite the fractions with this common denominator, resulting in the fractions 4/12 and 6/12. We can then compare the numerators 4 and 6 to determine that the fraction 2/4 is larger than the fraction 1/3.
In addition to representing division problems and being used in fraction arithmetic, fractions are also commonly used to express ratios.
A ratio compares two or more quantities of the same nature, and it is often written in the form of a fraction. For example, in a group, the ratio of men to women could be expressed as 3/5, which means that for every 3 men, there are 5 women.
The Role of the Denominator in Different Mathematical Operations
We can perform many operations on fractions, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. To add or subtract fractions, though, they must have the same denominator. For example, the fractions “1/4” and “3/4” can be added by adding the numerators, resulting in the fraction “4/4,” which can be simplified to “1.”
To multiply fractions, the numerators are multiplied, and the denominators are multiplied. For example, the product of the fractions “1/2” and “1/3” is “1/6.” To divide fractions, the second fraction is inverted and then multiplied by the first fraction.
For example, the division of the fractions “1/2” and “1/3” is the same as multiplying “1/2” by “3/1,” which is “3/2.”
Advantages of the Numerator
A numerator in mathematics is the part of a fraction that represents the number of parts of a whole being considered. It is located above the fraction line and is used in combination with the denominator to represent quantities that are not whole numbers.
Fractions can be simplified, added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided, and are useful for representing ratios, proportions, and decimals.
Overall, the numerator plays a crucial role in the representation and manipulation of fractions in mathematics. It represents the number of parts being considered in a fraction and is used in a variety of mathematical operations, including simplification, conversion, comparison, and the expression of ratios.
| Fraction | Denominator | Numerator |
| 5/9 | 9 | 5 |
| (a+b)/c | c | (a+b) |
| 1/1 | 1 | 1 |
| 10x/y | y | 10x |
| 4/(3+5) | (3+5) | 4 |
| a/c | c | a |
| (2x + 3y) / (z – 3) | (z – 3) | (2x + 3y) |
| (2i + j + 5k) / (5x + 7y + z) | (5x + 7y + z) | (2i + j + 5k) |
Solved Examples Based on Real-life Problems
Example 1
Jon picked 4 balls from a box containing 20 balls of different colors and qualities. Write this scenario in the form of a fraction and mention the numerator from the Fraction.

Figure 3 – A box containing different balls
Solution
The total number of balls in the box = 30
The number of Balls picked by Jon = 4
From the given data:
Jon picked 4/20th of the different balls from the box
So, 4/20 is the fractional form of data in the given scenario. Hence, 4 is the numerator of this fraction as it is above the fractional line.
Example 2
Jim’s father went to a fruit shop and bought 30 bananas. His father gave him 5 bananas from the bag. What fraction of bananas Jim’s father is left with? The resultant fraction will have a numerator and a denominator, indicating each of them.
Solution
The total number of bananas bought by Jim’s father = 30.
The number of mangoes given to his son Jim = 5.
The number of bananas left = 30– 5= 25.
The fraction of mangoes the father of Jim was left with = 25/30 = 5/6.
Thus, the fraction of bananas left with the father of Jim is 5/6.
In this fraction:
5 is numerator
6 is denominator
All mathematical images are generated using GeoGebra.
