– $ P (z \space \leq \space – \space 1.0 )$
– $ P (z \space \geq \space – \space 1 )$
– $ P (z \space \geq \space – \space 1.5 )$
– $ P ( – \space 2.5 \space \geq \space \space z )$
– $ P (- \space 3 \space < \space z \space \geq \space \space 0 )$
The main objective of this question is to find the probabilities for the given expressions given the z score, which is a standard random variable.
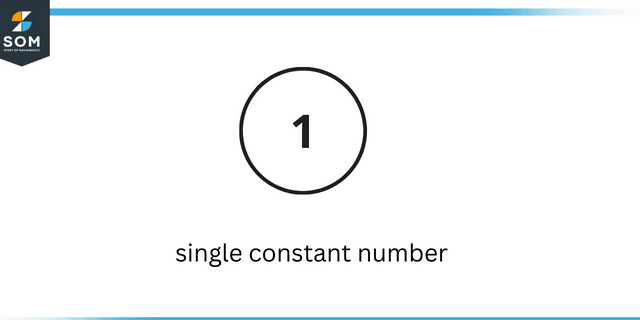
Single constant number

Random number
This question uses the concept of z-score. The standard normal z-table is the abbreviation for the z-table. Standard Normal models are used in hypothesis testing as well as the differences between two means. $100 \space % $ of an area under a distribution of normal curve is represented by a value of one hundred percent or $ 1 $. The z-table tells us how much of the curve is below a given point. The z-score is calculated as:
\[ \space z \space = \frac{ score \space – \space mean }{ standard deviation} \]
Probability
Expert Answer
We have to compute the probabilities.
a) From the z-table, we know that the value of $ – \space 1 $ is:
\[ \space = \space 0.1587 \]
So:
\[ \space P (z \space \leq \space – \space 1.0 ) \space = \space 0.1587 \]
b) Given that:
\[ \space P (z \space \geq \space – \space 1 ) \]
Thus:
\[ \space = \space 1 \space – \space P (z \space \leq \space – \space 1 ) \]
We know that:
\[ \space P (z \space \leq \space – \space 1.0 ) \space = \space 0.1587 \]
So:
\[ \space = \space 1 \space – \space 0.1587 \]
\[ \space = \space 0.8413 \]
c) Given that:
\[ \space P (z \space \geq \space – \space 1.5 ) \]
So:
\[ \space = \space 1 \space – \space P(z \space \leq \space – \space 1.5 \]
\[ \space = \space 1 \space – \space 0.0668 \]
\[ \space = \space 0.9332 \]
d) Given that:
\[ \space P ( – \space 2.5 \space \geq \space \space z ) \]
So:
\[ \space P(z \space \geq \space – \space 2.5) \]
\[ \space 1 \space – \space P(z \space \leq \space – \space 2.5) \]
\[ \space = \space 1 \space – \space 0.0062 \]
\[ \space = \space 0.9938 \]
e) Given that:
\[ \space P (- \space 3 \space < \space z \space \geq \space \space 0 ) \]
So:
\[ \space P(z \space \leq \space 0) \space – \space P(z \leq \space – \space 3) \]
\[ \space 0.5000 \space – \space 0.0013 \]
\[ \space = \space 0.4987 \]
Numerical Answer
The probability for the $ P (z \space \leq \space – \space 1.0 )$ is:
\[ \space = \space 0.1587 \]
The probability for the $ P (z \space \geq \space – \space 1 ) $ is:
\[ \space = \space 0.8413 \]
The probability for the $ P (z \space \geq \space – \space 1.5 )$ is:
\[ \space = \space 0.9332 \]
The probability for the $ P ( – \space 2.5 \space \geq \space \space z )$ is:
\[ \space = \space 0.9938 \]
The probability for the $ P (- \space 3 \space < \space z \space \geq \space \space 0 )$ is:
\[ \space = \space 0.4987 \]
Example
Find the probability for $ z $ which is a standard random variable.
\[ \space P (z \space \leq \space – \space 2.0 ) \]
We have to compute the probabilities. From the z-table, we know that the value of $ – \space 2 $ is:
\[ \space = \space 0.228 \]
So:
\[ \space P (z \space \leq \space – \space 1.0 ) \space = \space 0.228 \]
