What Is 7/15 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 7/15 as a decimal is equal to 0.466.An important concept in mathematics is Fractions, which help us determine if we want to divide an object or thing into different parts, how we can divide it, and what the magnitude or size of each piece will be. It is represented by two numbers that are divided to find the answer. For example, the solution of a fraction of 5/2 tells us that if we want to divide the number 5 into two equal parts, each part will be similar to 2.5.A standard method to solve a fraction is Division. Most of the time, students think Division is complicated, but some tricks and techniques are used to make this operation simple and easy.Division converts fractions into decimal numbers, which are preferred to be used in calculations because of their convenience and better understanding. For example, 3.5 is a decimal number equivalent to 7/2 and is easier to understand than its fraction.Now we will try to solve a fraction of 7/15 by the Long Division method.
The fraction 7/15 as a decimal is equal to 0.466.An important concept in mathematics is Fractions, which help us determine if we want to divide an object or thing into different parts, how we can divide it, and what the magnitude or size of each piece will be. It is represented by two numbers that are divided to find the answer. For example, the solution of a fraction of 5/2 tells us that if we want to divide the number 5 into two equal parts, each part will be similar to 2.5.A standard method to solve a fraction is Division. Most of the time, students think Division is complicated, but some tricks and techniques are used to make this operation simple and easy.Division converts fractions into decimal numbers, which are preferred to be used in calculations because of their convenience and better understanding. For example, 3.5 is a decimal number equivalent to 7/2 and is easier to understand than its fraction.Now we will try to solve a fraction of 7/15 by the Long Division method.Solution
To solve any fraction, we must first separate its parts based on their respective functions, and we get our dividend and divisor. In the example given below, we have 7 to divide by 15, so 7 is the dividend and 15 is the divisor.Dividend = 7
Divisor = 15
The decimal value we acquire after the Division of two numbers is our final result, and we call it the Quotient.Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 7 $\div$ 15
If we have two such numbers which cannot be divided completely, we get a value left behind at the end of the Division. This value is named Remainder.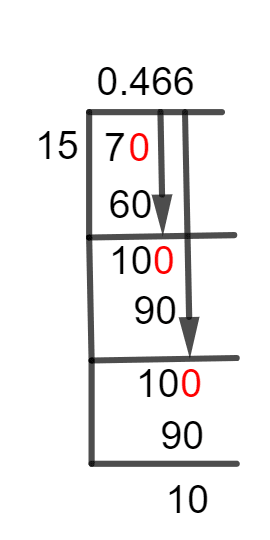
Figure 1
7/15 Long Division Method
We have to find the solution of:7 $\div$ 15
A decimal point must be present in the Quotient since our dividend, 7, is smaller than our divisor, 15. By multiplying 7 with 10, we can generate this decimal point. This multiplication yields 70 as a dividend.70 $\div$ 15 \approx 4
15 x 4 = 60
70 – 60 = 10 is determined to be the remainder.The remainder is multiplied by 10 to give us 100 because it is smaller than the divisor.100 $\div$ 15 \approx 6
15 x 6 = 90
We are again left with a value of 10.100 – 90 = 10
As a result, our subsequent computations will be identical to those from the previous phase.100 $\div$ 15 \approx 6
15 x 6 = 90
100 – 90 = 10
The exact value of the remainder indicates that it is a recurring and Non-Terminating fraction and has a decimal value of 0.466. Non-terminating decimals are produced when a fraction is stated in decimal form and always has a remainder, regardless of how extensively the extended division technique is applied.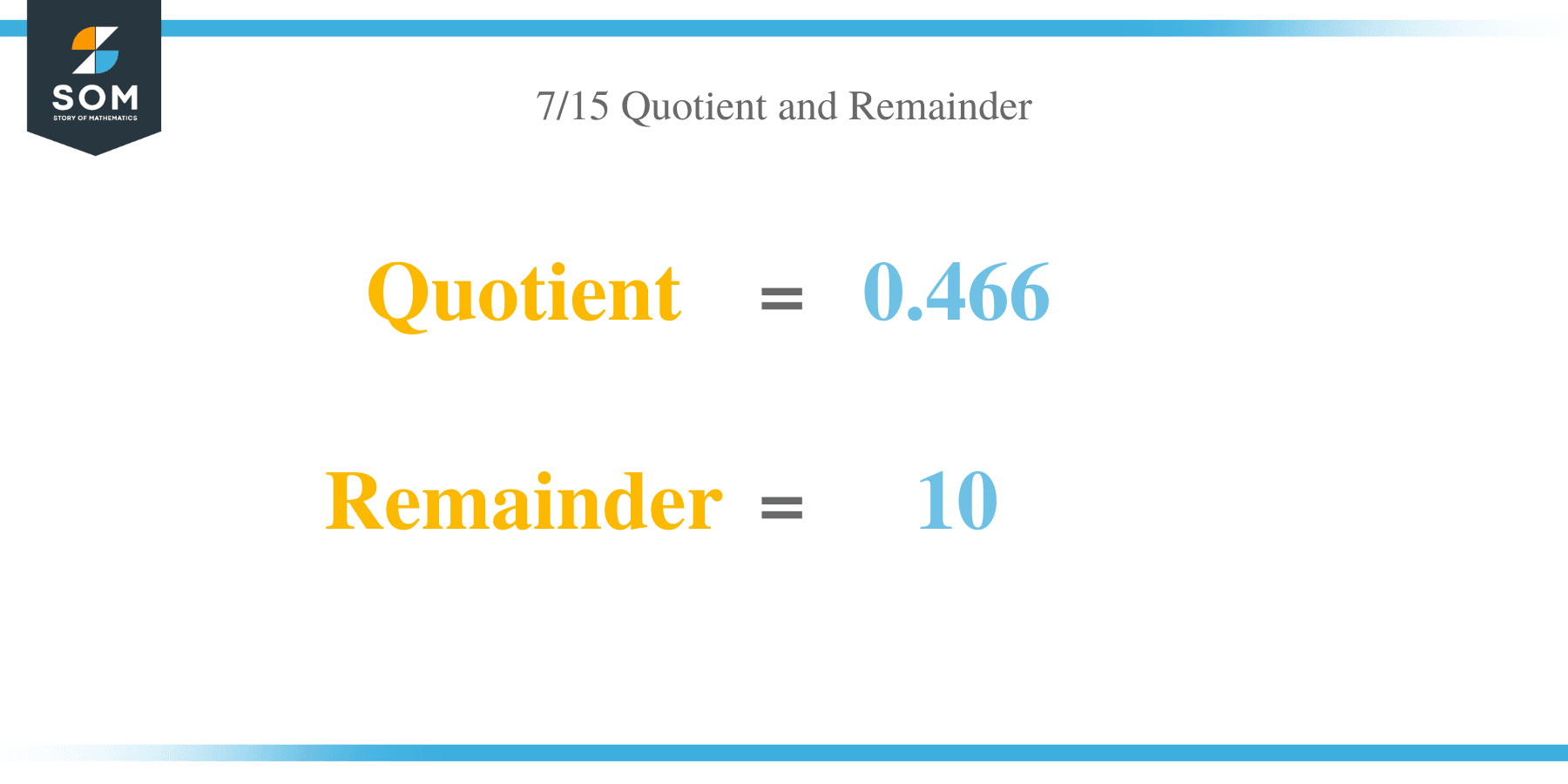 Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.