What Is 1/8 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 1/8 as a decimal is equal to 0.125.A Fraction can describe a division between two numbers when they cannot be Divided across one another using the traditional methods. But if you were to solve said division, it would result in a Decimal Value, as the numbers are not multiplicatively related.A Decimal Value contains two parts, one being the Whole Number part whilst the other being the Decimal part. Thus, a Fraction will represent a decimal value as a result of its division. And to solve this division, the method used is called Long Division.Now, let’s look at the Long Division solution of this fraction 1/8.
The fraction 1/8 as a decimal is equal to 0.125.A Fraction can describe a division between two numbers when they cannot be Divided across one another using the traditional methods. But if you were to solve said division, it would result in a Decimal Value, as the numbers are not multiplicatively related.A Decimal Value contains two parts, one being the Whole Number part whilst the other being the Decimal part. Thus, a Fraction will represent a decimal value as a result of its division. And to solve this division, the method used is called Long Division.Now, let’s look at the Long Division solution of this fraction 1/8.Solution
We begin by transforming a Fraction into its corresponding Division. That is done by converting a fraction’s constituents into a division’s constituents. Thus, the numerator of the fractions becomes the Dividend, and the fraction’s denominator becomes the Divisor.Dividend = 1
Divisor = 8
Now, the quantity Quotient is associated with the solution of the division, and it is exactly what we are interested in. The Quotient’s relationship with the Dividend and the Divisor is therefore given as follows:Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor= 1 $\div$ 8
Without further ado, let’s solve our fraction to the decimal problem using the Long Division Method: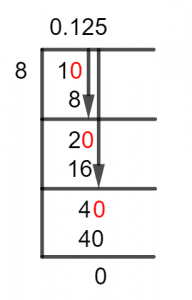
Figure 1
1/8 Long Division Method
The Long Division Method is based on the concept of solving the division in parts, thus we keep changing our Dividend to get the solution to our problem.To get a better understanding of the process, we will introduce the quantity referred to as the Remainder. The Remainder is what gets left behind when a division occurs, and the unique thing about it in terms of the Long Division method is that it then becomes the new Dividend.Now, let’s begin solving our problem, i.e., fraction 1/8.As we can see that the dividend is smaller than the divisor, the fraction is Proper, and the Quotient will be smaller than 1. So, we introduce a Zero to the dividend using the decimal, and the dividend becomes 10.10 $\div$ 8 $\approx$ 1
Where:8 x 1 = 8
Here, a Remainder equal to 10 – 8 = 2 is produced. Hence, we repeat the process of adding a zero, and getting 20 as the new dividend:20 $\div$ 8 $\approx$ 2
Where:8 x 2 = 16
This time a Remainder of 4 is produced, as we have gone through two iterations, we repeat the process once more to get a third decimal place solution. Thus, we have a new dividend equal to 40:40 $\div$ 8 = 5
Where:8 x 5 = 40
Thus, we have a Quotient equal to 0.125 as there was no Remainder produced. This quotient was also produced by adding up all the quotients from each division.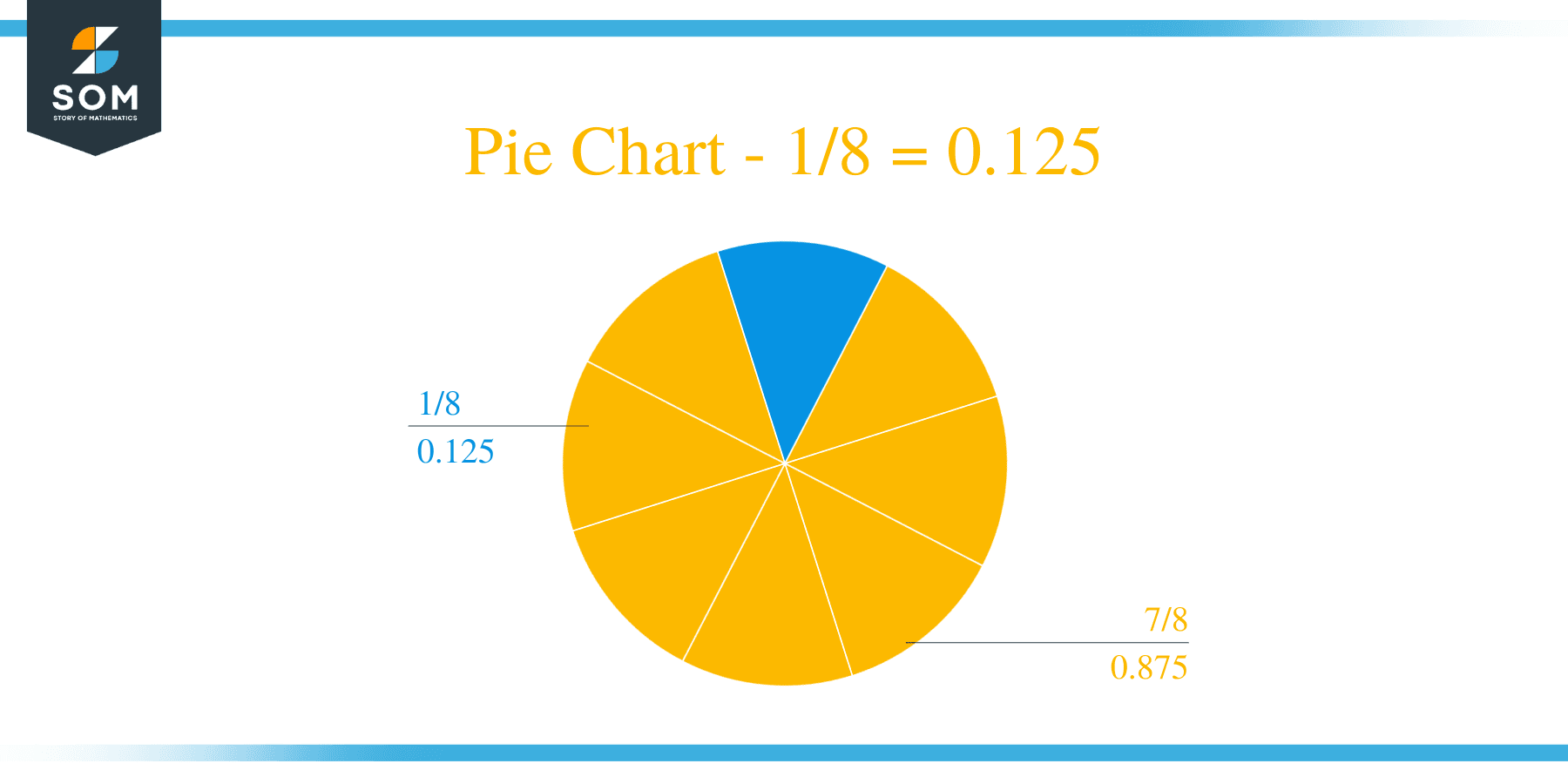 Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.