JUMP TO TOPIC
 The derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ is equal to $\dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$.
The derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ is equal to $\dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$.
Mathematically, the formula is written as $\dfrac{d}{dx} tan ^{-1} x = (tan^{-1}x)^{‘} = \dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$. We are basically differentiating the inverse function of a tangent with respect to the variable “$x$”.
In this topic, we will study the derivative of the inverse of tan x and its proof by using the first principle/abnitio method and through implicit differentiation. We will also study several examples so that you fully understand the topic.
What Is the Derivative of Tan^-1 x?
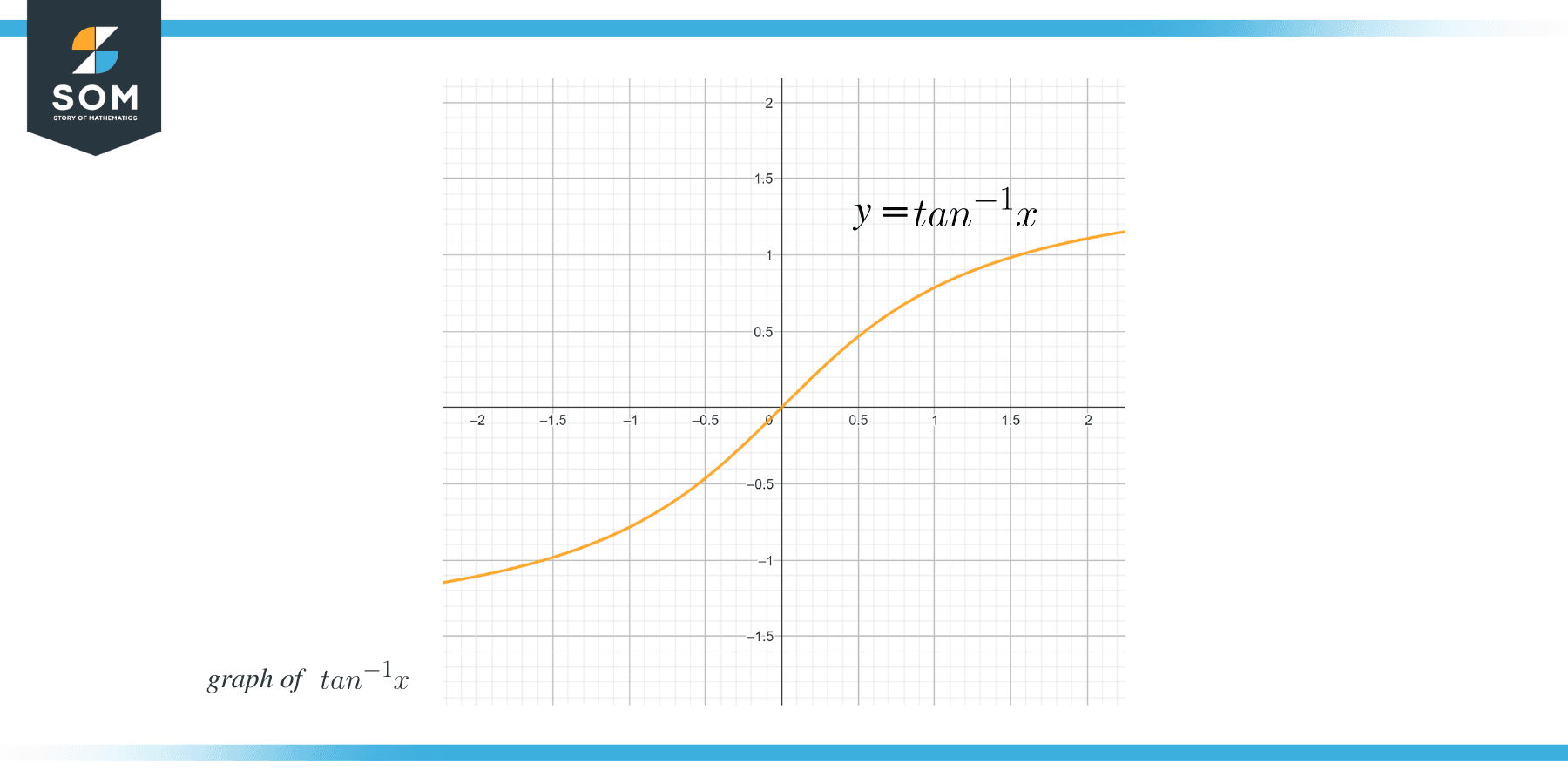
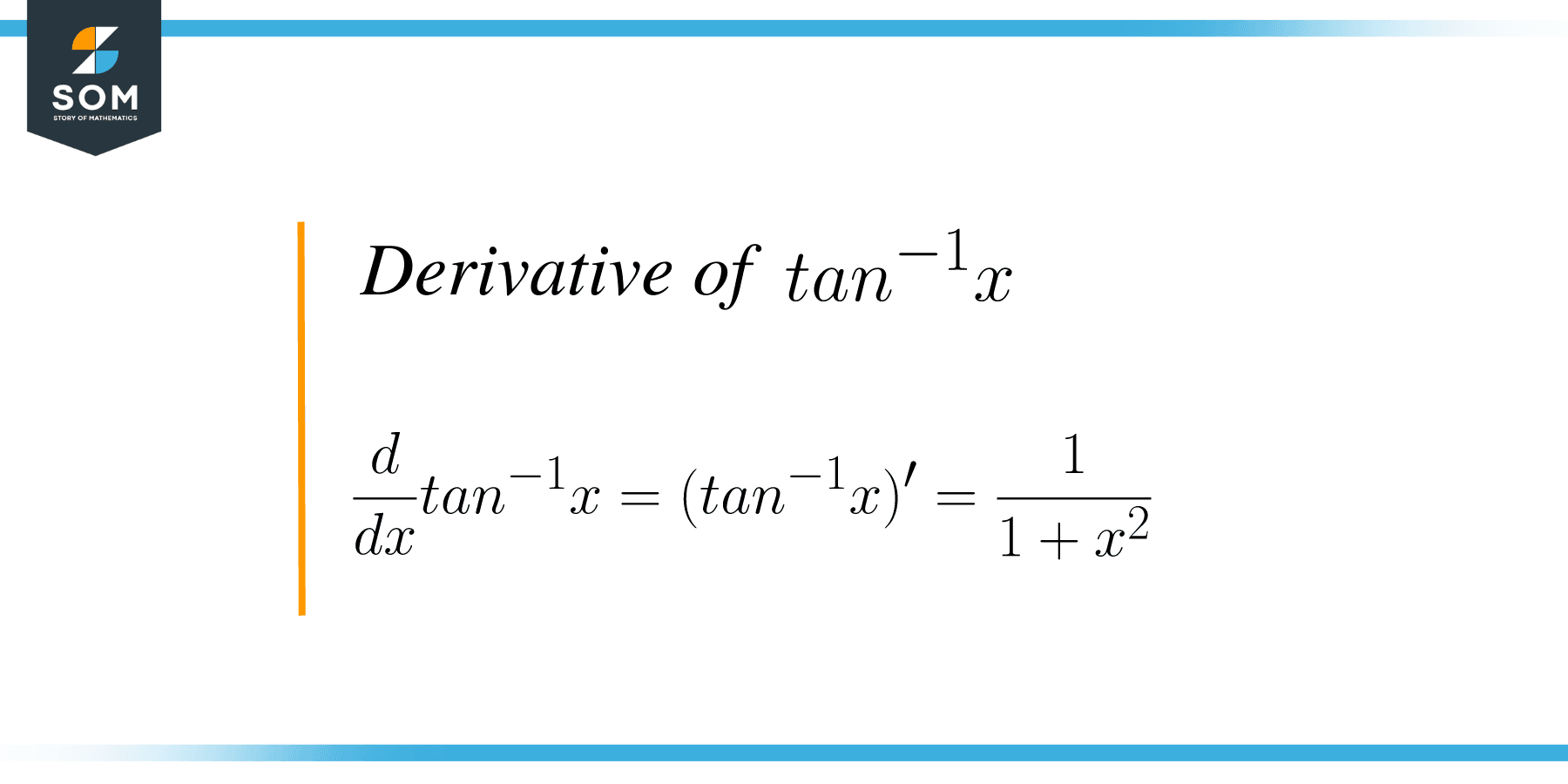 The derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ or arc tan(x) is the process of differentiating the arc tan trigonometric function with respect to “x”. Tangent is a trigonometric function, and if we take the inverse of this function, then it is called the inverse tangent function or arc tan function. The graph for the inverse tangent function is given as:
The derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ or arc tan(x) is the process of differentiating the arc tan trigonometric function with respect to “x”. Tangent is a trigonometric function, and if we take the inverse of this function, then it is called the inverse tangent function or arc tan function. The graph for the inverse tangent function is given as:
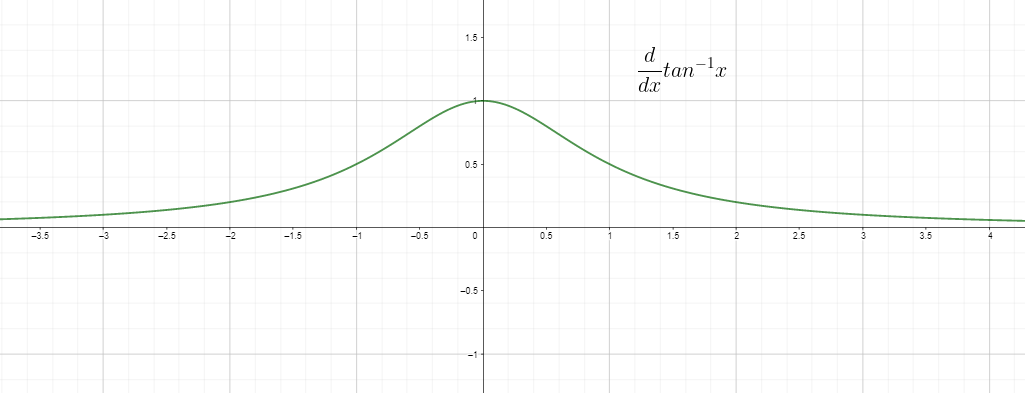
Differentiating is basically the rate of change, so we can call the $\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{1}x$ as the rate of change of inverse/arc tangent with respect to “$x$” and it is equal to $\dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$. The graph for derivative of the tan inverse is given as:
Formula of Derivative Tan^-1 x
The formula for the derivative of tan inverse x is given as:
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1} x = \dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$
It is imperative that you learn and memorize all the derivative formulas for all the inverse trigonometric functions because memorizing the formula of one inverse function will help you in memorization of the formula for another inverse/arc trigonometric function.
For example, in this case, the formula for inverse tan x is the same as the inverse cot x, the only difference is the negative sign, so if you know the formula for inverse cot x, then by removing the negative sign you will get the formula for inverse tan x.
Different Methods To Calculate Derivative of Tan^{-1}x
There are many methods which can be used to determine the derivative of $tan^{-1}x$, and some of them are listed below.
- Derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ using the first principle method
- Derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ using the implicit differentiation method
- Derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ using the cot Inverse formula
Derivative of Tan^-1 x Using First Principle Method
The first principle method can be used to derive the proof of $(tan^{-1})^{‘}$. The first principle method does not use other theorems. It uses the definition of derivative to solve any function. The general formula of the first principle method for a function f(x) is given as:
$f^{‘}(x) = \lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{f(x+h) –f(x)}{h}$
So by using this definition of the derivative, we will prove that derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ is equal to $\dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$.
Proof
$f(x) = tan^{-1}x$
$f^{‘}(x) = \dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}x = f^{‘}(x) = \lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{tan(x+h) – tan(x)}{h}$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}x = f^{‘}(x) = \lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{tan^{-1}(x+h) – tan^{-1}(x)}{h}$
We know that $tan^{-1} a – tan^{-1} b = tan^{-1} (\dfrac{a – b}{1+ ab})$
Now applying this formula to $tan^{-1}(x+h) – tan^{-1}(x)$ where $a = (x+h)$ and $b = x$, we will get:
$f^{‘}(x) = \lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{tan^{-1}(\frac{x+ h -x}{1+ x (x+h)}) }{h}$
So by cancelling “$x$” and “$-x$” in the numerator, we will get:
$f^{‘}(x) = \lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{tan^{-1}(\frac{ h }{1+ x (x+h)}) }{h}$
Divide and multiply the above expression with $\dfrac{1}{1+ x (x+h)}$.
$f^{‘}(x) = \lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{tan^{-1}(\frac{h}{1+ x (x+h)}) }{\frac{h}{1+ x (x+h)}} \times \dfrac{1}{1+ x (x+h)}$
We know that $\lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{tan^{-1}h}{h} = 1$
In our case, the upper and lower angle expression $\frac{h}{1+ x (x+h)}$ is the same for $tan^{-1}$. Hence $\lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{tan^{-1}(\frac{h}{1+ x (x+h)}) }{\frac{h}{1+ x (x+h)}}$. The expression will be equal to 1.
$f^{‘}(x) = 1 \times \dfrac{1}{1+ x (x + 0)}$
$f^{‘}(x) = 1 \times \dfrac{1}{1+ x (x)}$
$f^{‘}(x) = \dfrac{1}{1+ x^{2}}$
Hence, we have proved that the derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ is equal to $\dfrac{1}{1+ x^{2}}$ by using the first principle method.
Derivative of Tan^-1 x Using Implicit Differentiation Method
The derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ can be determined using the implicit differentiation method. According to implicit differentiation, if we are given an implicit function, then we take the derivative of the left-hand side and right side hand of the equation with respect to the independent variable.
In this case, the original function can be written as $y = tan^{-1}x$. Here, “$x$” is the independent variable. We will re-write the equation as:
$x = tan (y)$ Here $x = tan(tan^{-1}x)$
Proof
$f(x) = y = tan^{-1}x$
$x = tan y$
Taking derivative on both sides with respect to “x.”
$\dfrac{dx}{dx} = \dfrac{d tan(y)}{dx}$
$1 = \dfrac{d tan(y)}{dx}$
Multiplying and dividing the right-hand side “$dy$.”
$1 = \dfrac{d tan(y)}{dx} \times \dfrac{dy}{dy}$
$1 = \dfrac{d tan(y)}{dy} \times \dfrac{dy}{dx}$
$1 = sec^{2} \times \dfrac{dy}{dx}$
We know that according to trigonometric identity:
$sec^{2} – tan^{2}x = 1$
$sec^{2} = 1 +tan^{2}$
$1 = [1 + tan^{2}y] \dfrac{dy}{dx}$
$\dfrac{dx}{dy} = 1 + tan^{2}y$
$\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{1}{1 + tan^{2}y}$
We know tan $y = x$ so, $tan^{2}y = x^{2}$
$\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{1}{1 + x^{2}}$
Hence, we have proved that the derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ is equal to $\dfrac{1}{1+ x^{2}}$ by using the implicit differentiation method.
Derivative of Tan^-1 x Using Cot^-1 x Function
The derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ can also be determined by using another trigonometric inverse function of $cot^{-1}x$. We will prove that $tan^{-1}x$ is equal to $\dfrac{1}{1+ x^{2}}$ by using the function $cot^{-1}x$. We will differentiate $tan^{1}x$ with respect to $cot^{1}x$.
Proof
$f(x) = y = tan^{-1}x$
$x = tan y$
Taking derivative on both sides with respect to “$x$”
$\dfrac{dx}{dx} = \dfrac{d tan(y)}{dx}$
$1 = \dfrac{d tan(y)}{dx}$
Multiplying and dividing the right-hand side “$dy$.”
$1 = \dfrac{d tan(y)}{dx} \times \dfrac{dy}{dy}$
$1 = \dfrac{d tan(y)}{dy} \times \dfrac{dy}{dx}$
$1 = sec^{2}y \times \dfrac{dy}{dx}$
$\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{1}{ sec^{2}} = \dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$
Let $g = cot^{-1}x$
$x = cot g$
Now differentiating the above function with respect to “$x$”
$\dfrac{dx}{dx} = \dfrac{d cot(g)}{dx}$
$1 = \dfrac{-cosec ^{2}g)}{dx}$
Multiplying and dividing by “$dg$”
$1 = \dfrac{-cosec ^{2}g)}{\dfrac{dg}{dx}}$
$\dfrac{dg}{dx} = – \dfrac{1}{1 + cosec^{2}g}$
According to the trigonometric identity, we know that.
$cosec^{2}x – cot^{2}x = 1$
$cot^{2}x = 1 + cosec^{2}x$
$\dfrac{dg}{dz} = – \dfrac{1}{1 + x^{2}}$
$\dfrac{dx}{dg} = – (1+x^{2})$
We need to find out the derivative of $tan^{-1}$ with respect to $cot^{-1}$, which is $\dfrac{dy}{dg}$.
$\dfrac{dy}{dg} = \dfrac{dy}{dx} \times \dfrac{dx}{dg}$
$\dfrac{dy}{dg} = (\dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}) \times [-(1+x^{2}]$
$\dfrac{dy}{dg} = -1$
We know that $\dfrac{d tan^{-1}x}{d cot^{-1}x} = -1$ and we have proved that the derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ with respect to $cot^{-1}x$ is $-1$. Hence, indirectly we can say that the derivative of $tan^{-1}x$ is $\dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$.
Example 1: Determine the following derivatives:
- Derivative of tan^-1(x^2)
- Derivative of tan^-1(x) at x = 1
- Derivative of tan inverse 1/x
- Derivative of tan^-1(x^3)
- Derivative of tan inverse x/y
Solution:
1).
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^-1(x^2) = \dfrac{2x}{1 + x^{4}}$
2).
We know
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^-1(x) = \dfrac{1}{1 + x^{2}}$
at $x = 1$
Derivative of $tan^-1(1)$ = $\dfrac{1}{1 + 1^{2}} = 1$
3).
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^-1(\frac{1}{x}) = – \dfrac{1}{1 + x^{2}}$
4).
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^-1(x^3) = \dfrac{3x}{1 + x^{6}}$
5).
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^-1(\frac{x}{y}) = \dfrac{y}{x^{2} + y^{2}}$
Example 2: Find the derivative of $tan^{-1}( 5x – 2)$ by using the derivative formula of tan inverse x.
Solution:
We know that the formula for derivative of $tan^{-1}x = \dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$, but if we write it in detail, it is written as $\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}x = \dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$. $\dfrac{d}{dx}. x = \dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}. 1 = \dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}$
By using the chain rule, we will find out the $tan^{-1}( 5x – 2)$.
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}( 5x – 2) = \dfrac{1}{1+ [5x-2]^{2}}. \dfrac{d}{dx} (5x -2)$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}( 5x – 2) = \dfrac{1}{1+ [5x-2]^{2}}. (5 – 0)$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}( 5x – 2) = \dfrac{5}{1+ [5x-2]^{2}}$
Example 3: Find the derivative of $tan^{-1}( 8x + 3)$ by using the derivative formula of tan inverse x.
Solution:
By using the chain rule, we will find out the $tan^{-1}(8x + 3)$.
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}( 5x – 2) = \dfrac{1}{1+ [8x +3 ]^{2}}. \dfrac{d}{dx} (8x + 3)$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}( 5x – 2) = \dfrac{1}{1+ [8x + 3]^{2}}. (8 + 0)$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}( 5x – 2) = \dfrac{8}{1+ [8x + 3]^{2}}$
Example 4: Find the derivative of $x^{2}.tan^{-1}(x)$ by using the derivative formula of tan inverse x.
Solution:
By using the chain rule, we will find out the $x^{2}.tan^{-1}(x)$.
$\dfrac{d}{dx} x^{2}.tan^{-1}( x ) = \dfrac{d}{dx} x^{2}. tan^{-1}x + x^{2}. \dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}x$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}( 5x – 2) = 2x. tan^{-1}x + x^{2}. \dfrac{1}{1 + x^{2}} \dfrac{d}{dx}.x$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1}( 5x – 2) = 2x. tan^{-1}x + x^{2}. \dfrac{1}{1 + x^{2}}$
Example 5: Find the derivative of $8x^{2}.tan^{-1}( 4x + 3)$ by using the derivative formula of tan inverse x.
Solution:
By using the chain rule, we will find out the $8x^{2}.tan^{-1}( 4x + 3)$.
$\dfrac{d}{dx} 8x^{2}.tan^{-1}(4x+ 3) = \dfrac{d}{dx} 8x^{2}. tan^{-1} ( 4x + 3) + 8x^{2}. \dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1} ( 4x + 3)$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} 8x^{2}.tan^{-1}(4x+ 3) = 16x . tan^{-1}( 4x + 3) + 8x^{2}. \dfrac{1}{1 + (4x +3)^{2}} \dfrac{d}{dx}.(4x +3)$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} 8x^{2}.tan^{-1}(4x+ 3) = 16x . tan^{-1}( 4x + 3) + 8x^{2}. \dfrac{1}{1 + (4x +3)^{2}} . 4$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} 8x^{2}.tan^{-1}(4x+ 3) = 16x . tan^{-1}( 4x + 3) + 32x^{2}. \dfrac{1}{1 + (4x +3)^{2}}$
Practice Questions
1. Find the derivative of $5x^{3}.tan^{-1}(5x – 4)$ by using the derivative formula of tan inverse x.
2. If we are given a function $f(z) = z = tan^{-1} [\dfrac{2y}{1 – y^{2}}]$, determine the derivative $\dfrac{dy}{dz}$.
Answer Key:
1).
By using the chain rule, we will find out the $5x^{3}.tan^{-1}(5x – 4)$.
$\dfrac{d}{dx} 5x^{3}.tan^{-1}(5x – 4) = \dfrac{d}{dx} 5x^{3}. tan^{-1} (5x – 4) + 5x^{3}. \dfrac{d}{dx} tan^{-1} (5x – 4)$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} 5x^{3}.tan^{-1}(5x – 4) = 15x^{2} . tan^{-1}(5x – 4) + 5x^{3}. \dfrac{1}{1 + (5x – 4)^{2}} \dfrac{d}{dx}.(5x – 4)$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} 5x^{3}.tan^{-1}(5x – 4) = 15x^{2} . tan^{-1}(5x – 4) + 5x^{3}. \dfrac{1}{1 + (5x – 4)^{2}} . 5$
$\dfrac{d}{dx} 5x^{3}.tan^{-1}(5x – 4) = 15x^{2} . tan^{-1}(5x – 4) + 25 x^{2}. \dfrac{1}{1 + (5x – 4)^{2}}$
2).
Let us assume that y = tan x.
Then we can write the function $z = tan^{-1} [\dfrac{2y}{1 – y^{2}}]$ as:
$z = tan^{-1}[\dfrac{2 tan (x)}{1- tan^{2}(x)} ]$
We know that tan (2x) = $\dfrac{2 tan (x)}{1- tan^{2}(x)}$.
$z = tan^{-1}(tan (2x))$
$z = 2x$
putting the value of “x” in the above equation:
$z = 2 tan^{-1}y$
Taking derivative on both sides:
$z^{‘} = \dfrac{2}{1 + y^{2}}$
