- Home
- >
- Area of Polygons – Explanation & Examples
JUMP TO TOPIC
Area of Polygons – Explanation & Examples
 Whenever we talk about geometry, we talk about side lengths, angles, and areas of the shapes. We saw the other two before; let’s talk about the latter. You got to see so many mathematics exam questions regarding finding the shaded region of a particular polygon.
Whenever we talk about geometry, we talk about side lengths, angles, and areas of the shapes. We saw the other two before; let’s talk about the latter. You got to see so many mathematics exam questions regarding finding the shaded region of a particular polygon.
For that, you need to have the knowledge of formulas of area for different kinds of polygons.
In this article, you will learn:
- What the area of a polygon is
- How to find the area of a polygon, including the area of a regular and irregular polygon?
What is the Area of a Polygon?
In geometry, the area is defined as the region occupied inside the boundary of a two-dimensional figure. Therefore, the area of a polygon is the total space or region bound by the sides of a polygon.
The standard units for the measurement of the area are square meters (m2).
How to Find the Area of a Polygon?
Regular polygons such as rectangles, squares, trapeziums, parallelograms, etc., have pre-defined formulas for calculating their areas.
However, for an irregular polygon, the area is calculated by subdividing an irregular polygon into small sections of regular polygons.
Area of a regular polygon
Calculating a regular polygon area can be as simple as finding the area of a regular triangle. Regular polygons have equal side lengths and an equal measure of angles.
There are three methods of calculating the area of a regular polygon. Each method is used on different occasions.
Area of a polygon using the concept of the apothem
The area of a regular polygon can be calculated using the concept of apothem. The apothem is a line segment that joins the polygon’s center to the midpoint of any side that is perpendicular to that side. Therefore, the area of a regular polygon is given by;
A = 1/2 . p . a
where p = the perimeter of the polygon = sum of all the side lengths of a polygon.
a = apothem.
Consider a pentagon shown below;
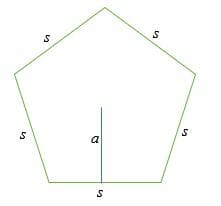
If the apothem, a = x and the length of each side of the pentagon is s, then the area of the pentagon is given by;
Area = 1/2 . p . a
Perimeter = s + s + s + s + s
= 5s
So, substitution,
Area = (½)5sx
= (5/2) (s. x) Sq. units
When using the apothem method, the length of the apothem will always be provided.
Area of a polygon using the formula: A = (L2 n)/[4 tan (180/n)]
Alternatively, the area of area polygon can be calculated using the following formula;
A = (L2 n)/[4 tan (180/n)]
Where, A = area of the polygon,
L = Length of the side
n = Number of sides of the given polygon.
Area of a circumscribed polygon
The area of a polygon circumscribed in a circle is given by,
A = [n/2 × L × √ (R² – L²/4)] square units.
Where n = number of sides.
L =Side length of a polygon
R = Radius of the circumscribed circle.
Let’s work out a few example problems about the area of a regular polygon.
Example 1
Find the area of a regular hexagon, each of whose sides measures 6 m.
Solution
For a hexagon, the number of sides, n = 6
L = 6 m
A = (L2n)/[4tan(180/n)]
By substitution,
A = (62 6)/ [4tan (180/6)]
= (36 * 6)/ [4tan (180/6)]
= 216/ [4tan (180/6)]
= 216/ 2.3094
A = 93.53 m2
Example 2
Find the area of a regular hexagon whose apothem is 10√3 cm and the side length are 20 cm each.
Solution
Area = ½ pa
First, find the perimeter of the hexagon.
p = (20 + 20 + 20 + 20 + 20 + 20) cm = (20 cm * 6)
= 120 cm
Substitute.
Area = ½ pa
= ½ *120 * 10√3
= 600√3 cm2
Example 3
Find the regular pentagon area if the polygon’s length is 8 m and the radius of the circumscribed circle is 7 m.
Solution
A = [n/2 × L × √ (R² – L²/4)] square units.
Where, n = 5; L = 8 m and R = 7 m.
By substitution,
A = [5/2 × 8 × √ (7² – 8²/4)] m2
= [20√ (49 – 64/4)]
= 20√ (49 – 16)
= 20√33 m2
= 20 * 5.745 m2
= 114.89 m2
Example 4
Find the area of a regular pentagon whose apothem and side length are 15cm and18 cm, respectively.
Solution
Area = ½ pa
a = 15cm
p = (18 * 5) = 90 cm
A = (½ * 90 * 15) cm
= 675 cm.
Area of an irregular polygon
An irregular polygon is a polygon with interior angles of different measures. The side lengths of an irregular polygon are also of different measure.
As said before, we can calculate the area of an irregular polygon by subdividing an irregular polygon into small sections of regular polygons.
Example 5
Find the area of an irregular polygon shown below if, AB = ED = 20 cm, BC = CD = 5cm and AB = BD = 8 cm
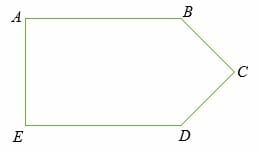
Solution
Subdivide the irregular polygon into sections of regular polygons
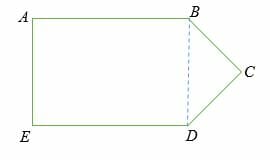
Therefore, ABED is a rectangle, and BDC is a triangle.
Area of rectangle = l * w
= 20 * 8 = 160 cm2
Area of the triangle = 1/2 . b . h
The height the triangle can be calculated by applying the Pythagoras theorem. For instance,
c2 = a2 + b2
252 = a2 + 42
a = √ (25 – 16)
a = 3
A = ½bh = ½ * 3 * 8
= 6 cm2
Now add the partial areas.
Area of polygon = (160 + 6) cm2 =166 cm2
