- Home
- >
- 45°-45°-90° Triangle – Explanation & Examples
45°-45°-90° Triangle – Explanation & Examples
 Now that we know what a right triangle is and what the special right triangles are, it is time to discuss them individually. Let’s see what a 45°-45°-90° triangle is.
Now that we know what a right triangle is and what the special right triangles are, it is time to discuss them individually. Let’s see what a 45°-45°-90° triangle is.
What is a 45°-45°-90° Triangle?
A 45°-45°-90° triangle is a special right triangle that has two 45-degree angles and one 90-degree angle. The side lengths of this triangle are in the ratio of;
Side 1: Side 2: Hypotenuse = n: n: n√2 = 1:1: √2.
The 45°-45°-90° right triangle is half of a square. This is because the square has each angle equal to 90°, and when it is cut diagonally, the one angle remains as 90°, and the other two 90° angles bisected (cut into half) and become 45° each.
The diagonal of a square becomes hypotenuse of a right triangle, and the other two sides of a square become the two sides (base and opposite) of a right triangle.
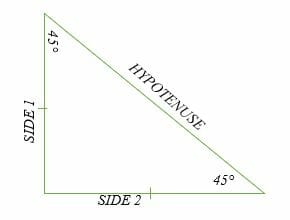
The 45°-45°-90° right triangle is sometimes referred to as an isosceles right triangle because it has two equal side lengths and two equal angles.
We can calculate the hypotenuse of the 45°-45°-90° right triangle as follows:
Let side 1 and side 2 of the isosceles right triangle be x.
Apply the Pythagorean Theorem a2 + b2 = c2, where a and b are side 1 and 2 and c is the hypotenuse.
x2 + x2 = 2x2
Find the square root of each term in the equation
√x2 + √x2 = √(2x2)
x + x = x √2
Therefore, the hypotenuse of a 45°; 45°; 90° triangle is x √2
How to Solve a 45°-45°-90° Triangle?
Given the length of one side of a 45°-45°-90° triangle, you can easily calculate the other missing side lengths without resorting to the Pythagorean Theorem or trigonometric methods functions.
Calculations of a 45°-45°-90° right triangle fall into two possibilities:
- Case 1
To calculate the length of hypotenuse when given the length of one side, multiply the given length by √2.
- Case 2
When given the length of the hypotenuse of a 45°-45°-90° triangle, you can calculate the side lengths by simply dividing the hypotenuse by √2.
Note: Only the 45°-45°-90° triangles can be solved using the 1:1: √2 ratio method.
Example 1
The hypotenuse of a 45°; 45°; 90° triangle is 6√2 mm. Calculate the length of its base and height.
Solution
Ratio of a 45°; 45°; 90° triangle is n: n: n√2. So, we have;
⇒ n√2 = 6√2 mm
Square both sides of the equation.
⇒ (n√2)2 = (6√2)2 mm
⇒ 2n2 = 36 * 2
⇒ 2n2 = 72
n2 = 36
Find the square root.
n = 6 mm
Hence, the base and height of the right triangle are 6 mm each.
Example 2
Calculate the right triangle’s side lengths, whose one angle is 45°, and the hypotenuse is 3√2 inches.
Solution
Given that one angle of the right triangle is 45 degrees, this must be a 45°-45°-90° right triangle.
Therefore, we use the n: n: n√2 ratios.
Hypotenuse = 3√2 inches = n√2;
Divide both sides of the equation by √2
n√2/√2 = 3√2/√2
n = 3
Hence, the length of each side of the triangle is 3 inches.
Example 3
The shorter side of an isosceles right triangle is 5√2/2 cm. What is the diagonal of the triangle?
Solution
An isosceles right triangle is the same as the 45°-45°-90° right triangle. So, we apply the ratio of n: n: n√2 to calculate the hypotenuse’s length.
Given that n = 5√2/2 cm;
⇒ n√2 = (5√2/2) √2
⇒ (5/2) √ (2 x 2)
⇒ (5/2) √ (4)
⇒ (5/2)2
= 5
Hence, the two legs of the triangle are 5 cm each.
Example 4
The diagonal of a 45°-45°-90°right triangle is 4 cm. What is the length of each of the legs?
Solution
Divide the hypotenuse by √2.
⇒ 4/√2
⇒ √4/√2
⇒ 4√2/2
= 2√2 cm.
Example 5
The diagonal of a square is 16 inches, calculate the length of the sides,
Solution
Divide the diagonal or hypotenuse by √2.
⇒ 16/√2
⇒ 16√2/√2 = 8√2
Hence, the length of the legs is 8√2 inches each.
Example 6
The angle of elevation of the top of a story building from a point on the ground 10 m from the base of the building is 45 degrees. What is the height of the building?
Solution
Given one angle as 45 degrees, assume a 45°- 45°-90°right triangle.
Apply the n: n: n√2 ratio where n = 10 m.
⇒ n√2 = 10√2
Therefore, the height of the building is 10√2 m.
Example 7
Find the length of the hypotenuse of a square whose side length is 12 cm.
Solution
To get the length of the hypotenuse, multiply the side length by √2.
⇒ 12 √2 = 10 √2
Hence, the diagonal is 10 √2 cm.
Example 8
Find the lengths of the other two sides of a square whose diagonal 4√2 inches.
Solution
A half of a square makes a 45°- 45°-90°right triangle. Therefore, we use the n: n: n√2 ratios.
n√2 = 4√2 inches.
divide both sides by √2
n = 4
Hence, the side lengths of the square are 4 inches each.
Example 9
Calculate the diagonal of a square flower garden whose side length is 30 m.
Solution
Apply the n: n: n√2 ratio, where n = 30.
⇒ n√2 = 30 √2
Therefore, the diagonal is equal to 30 √2 m
